Fig. 7.
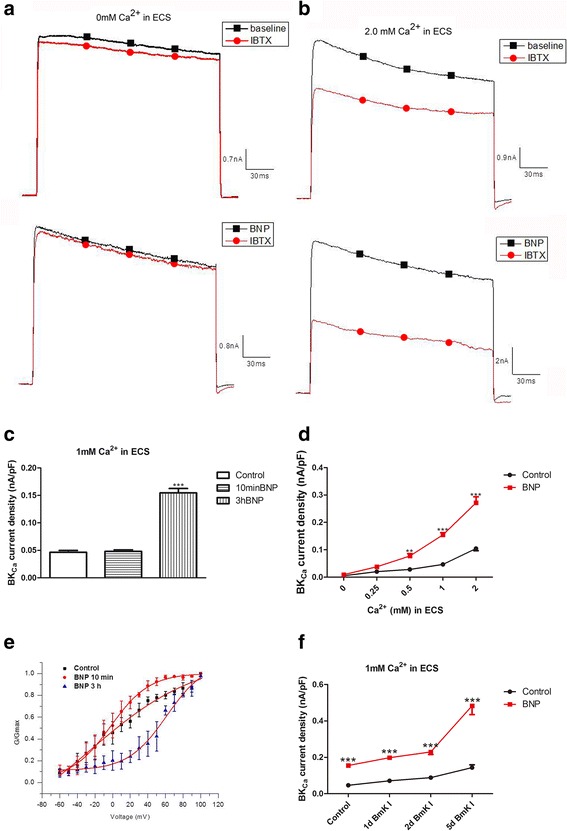
BNP increased the open probability of BKCa channels. a: An outward current in small DRG neurons were induced by a voltage ramp from −60 to 100 mV (0.2 s duration) in whole-cell voltage-clamp configuration. In Ca2+-free ECS BNP did not affect the current, IbTX did not change the current significantly either. b: In small DRG neurons incubated in ECS with 1 mM Ca2+, the current was elevated by pretreatment of BNP (100 ng/ml) for more than 2 h and was inhibited by BKCa channel inhibitor IbTX (100 nM). c: In small DRG neurons incubated in ECS with 1 mM Ca2+, BKCa current was elevated by pretreated with BNP (100 ng/ml) for 3 h (n = 7), but not by bath-applied BNP (100 ng/ml) for 10 min (n = 6). d: BKCa current was induced in small DRG neurons incubated in ECS with 0.5, 1 or 2 mM Ca2+, and this current was increased by pretreatment of BNP for 3 h (p < 0.01, n = 7 for 0.5 mM Ca2+ at 90 mV; p < 0.001, n = 7 for 1, 2 mM Ca2+ at 90 mV). In the presence of 0 or 0.25 mM extracellular Ca2+, BKCa current was not induced and BNP did not have effect (n = 7 neurons/group). BKCa current was calculated as the difference between total current and IBTX-resistant current, and was normalized to the cell membrane capacitance. e: G(V) relationship indicated that treatment of BNP for 10 min did not enhance the activation of BKCa currents which was significantly rightward shifted after treatment of BNP for 3 h. f: 1 day, 2 days and 5 days after i.pl. BmK I injection, BKCa current density of small DRG neurons were elevated significantly compared with control rats. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 versus control. Error bars indicated SEM
