Fig. 1.
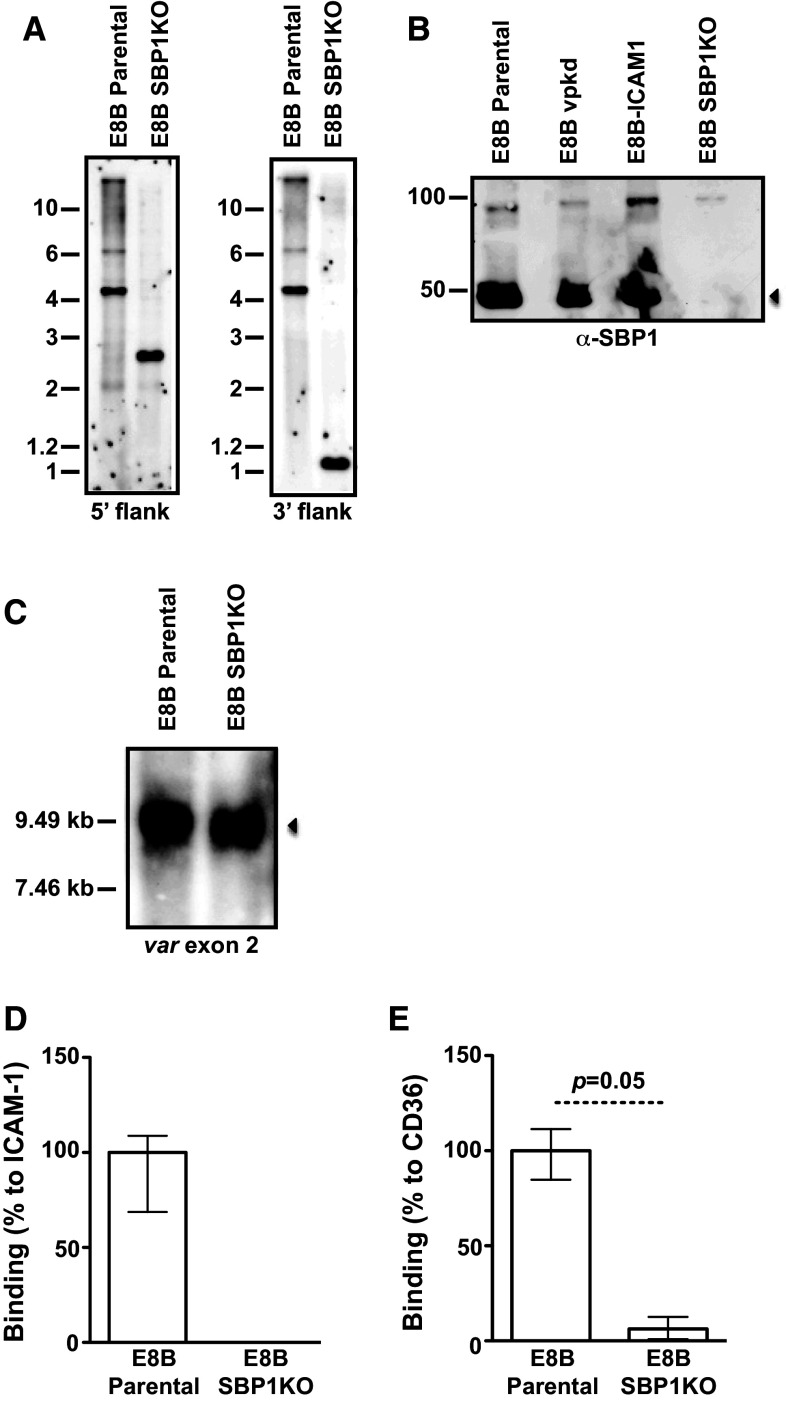
Phenotypic analyses of pfsbp1 knock-out (SBP1KO) parasites. a Southern blot analysis of the pfsbp1 locus in E8B parental and E8B SBP1KO parasites. Genomic DNA was digested with EcoRI/Bgl II and probed with the 5′ or 3′ targeting sequence. Predicted sizes for the plasmid were 6.9 kb (for both 5′ and 3′ probes) and 4.6 kb for E8B parental (for both 5′ and 3′ probes); predicted sizes for E8B SBP1KO were 2.7 kb (for 5′ probe) and 1.1 kb (for 3′ probe). b Western blot analyses of membrane extracts from mature trophozoite IEs probed with α-SBP1 antibodies. Antibodies detected SBP1 at approximately 50 kDa (arrow) in E8B parental, E8Bvpkd (PfEMP1 knock-down) and E8B-ICAM1 (parental line selected on ICAM1), which was absent in E8B SBP1KO. The band at 100 kDa present in all lanes corresponds to antibody cross reactivity. c Northern blot analysis of var gene transcription by hybridization with a specific var exon 2 sequence. The position of molecular weight standards (kb) is indicated on the left and the arrow represents var transcripts. In both E8B parental and E8B SBP1KO parasites, similar var transcripts were detected. RNA was extracted from highly synchronous ring stage IEs at approximately 10 h post-invasion. Adhesion of IEs to immobilized ICAM-1 (d) and CD36 (e) was substantially reduced in E8B SBP1KO compared to E8B parental. Values are expressed as a percentage of parental parasites binding to ICAM-1 or CD36. Assays were performed twice independently and bars represent median and interquartile ranges of samples tested in triplicate