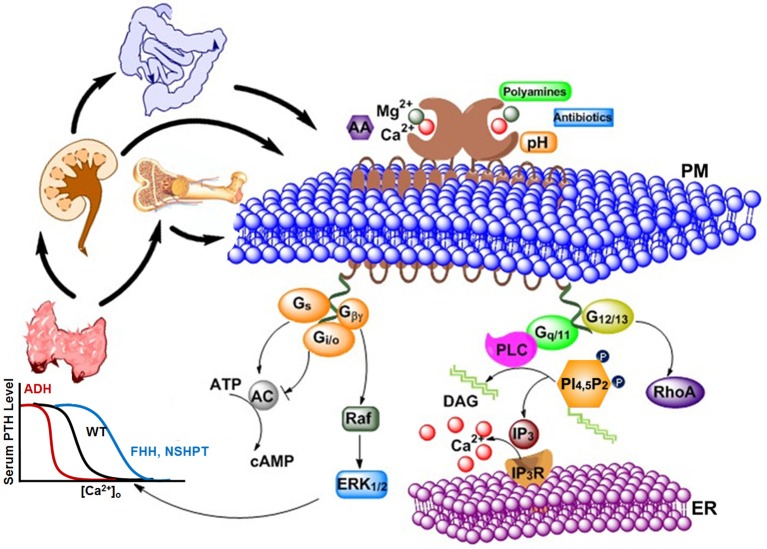
Figure 1.
Various types of agonists, including cations, peptides, amino acids, antibiotics, etc., can act on the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) to generate a complex intracellular signaling network. CaSR is also a pleiotropic receptor in its regulation of four G protein-mediated intracellular signaling pathways (Gq∕11, Gi∕o, Gs, and G12∕13). The correlations and crosstalk among different signaling cascades contribute the cooperative responses of intracellular calcium responses as well as parathyroid hormone (PTH) secretion (left) and intracellular calcium responses (right) to extracellular calcium. Bottom left: The sigmoidal relationship between calcium concentration in blood and PTH level in serum is demonstrated. Higher Ca2+ concentration is required for normal level of PTH in patients with familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia (FHH) or patients with Neonatal Severe Primary Hyperparathyroidism (NSHPT), as the response curve shifts to the right; on the other hand, lower Ca2+ concentration than normal is enough to trigger PTH secretion in patients with autosomal dominant hypocalcemia (ADH). PM, Plasma membrane; ER, Endoplasmic reticulum; AA, arachidonic acid; AC, adenylate cyclase; cAMP, cyclic AMP; DAG, diacylglycerol; ERK1∕2, extracellular-signal-regulated kinase; Gs, Gi∕o,G12∕13, and Gq∕11, subunits of the s-, i-, 12/13, and q-type alpha subunit of heterotrimeric G proteins, respectively; Gβγ, G beta and gamma complex; IP3, inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate; IP3R, inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor; PLC, phospholipase C; PI(4,5)P2, phoshatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate; RhoA, Ras homolog gene family, member A.