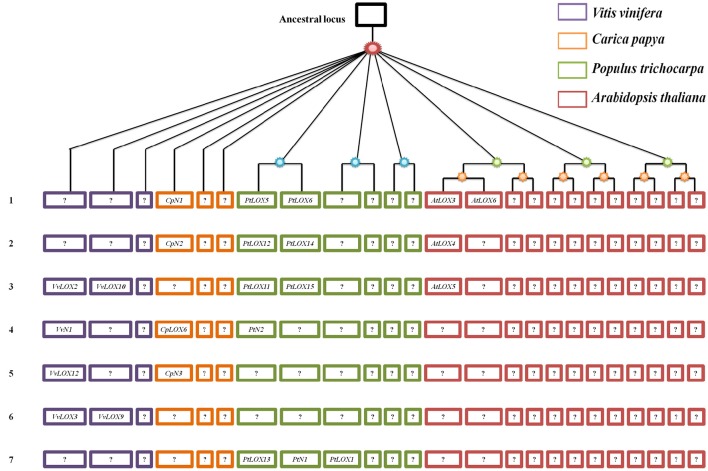
Figure 8.
Panoramic picture to visualize the differential retention and expansion of the ancestral LOXs associated with paleopolyploidy events that have occurred in four modern rosids. Square represents a SCB duplicated through paleopolyploidy events within and between species. Codes in the square correspond to associated LOX genes. Genes in the same line are thought to have originated from the same ancestral gene. Genes coded with an “N” between the letter and the number (e.g., CN1) represent those that have sub-functionalized into non-LOX; blank positions correspond to situations where the whole SCBs has been completely lost.