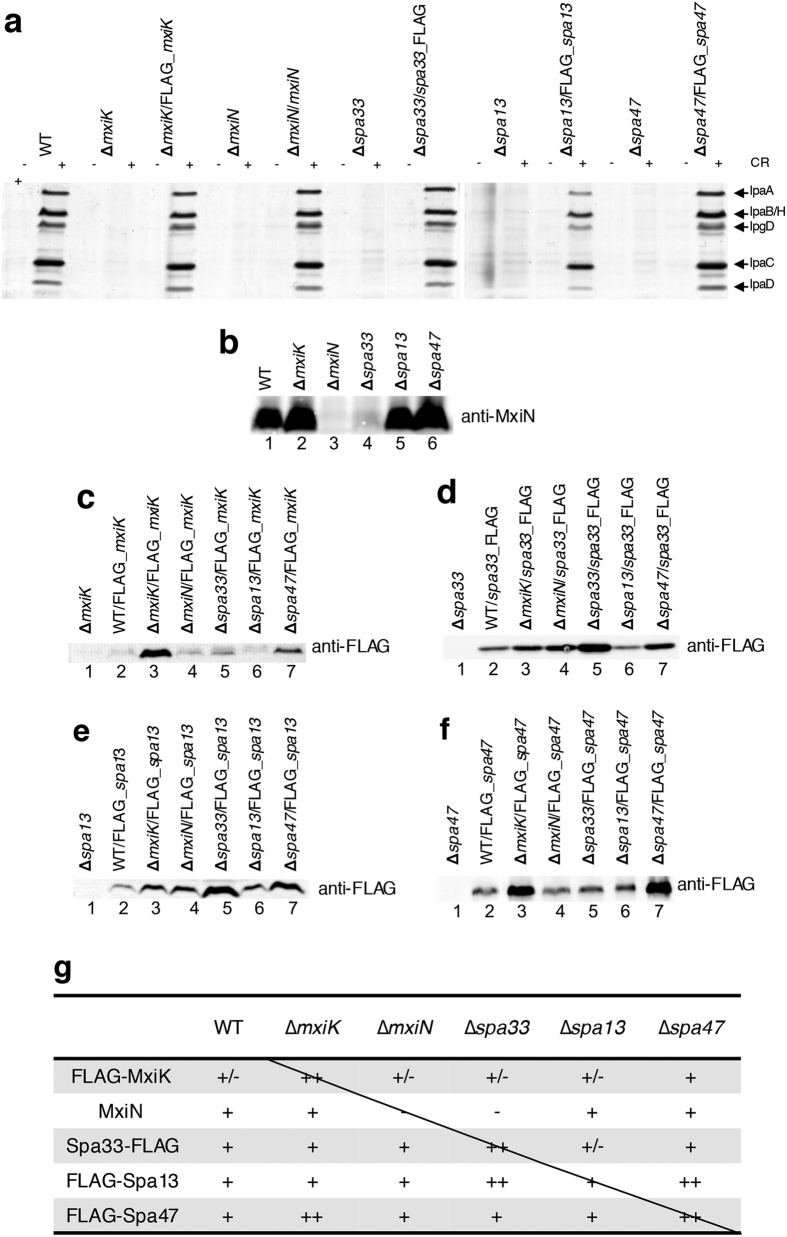
Figure 3. Analysis of the stability or expression of components of the Shigella T3SS cytoplasmic export apparatus in mutants of this portion of the apparatus.
(a) Complementation of cytoplasmic export apparatus knock mutants by in-trans expression of wild-type or FLAG-tagged proteins. Induced secretion of Ipa proteins in the presence (+) or absence (−) of Congo red (CR) was analysed by silver staining. The wild-type (WT) and the deletion mutants were used as controls, and bacterial numbers were normalized by optical density. The positions of the major Ipa proteins detected by silver staining are indicated on the side. The data shown here are representative of 2 independent experiments giving similar results. (b–f) Expression of native MxiN (b) and FLAG-tagged MxiK (c), Spa33 (d), Spa13 (e) and Spa47 (f) in different mutant backgrounds. Pellets of overnight grown cultures with equivalent bacterial numbers were analysed by immunoblotting with either a polyclonal rabbit antiserum against MxiN (b) or a monoclonal antibody against the FLAG tag (c–f), as indicated at the side. The data shown here are representative of 2 independent experiments giving similar results. The blots in b-f were cropped to show only the area where signal was detected. (g) Table semi-quantitatively summarising results of co-stability experiments in (b–f).