Figure 2. The effect of Bithionol on P. aeruginosa exotoxin A in human B-lymphoblastoid cells.
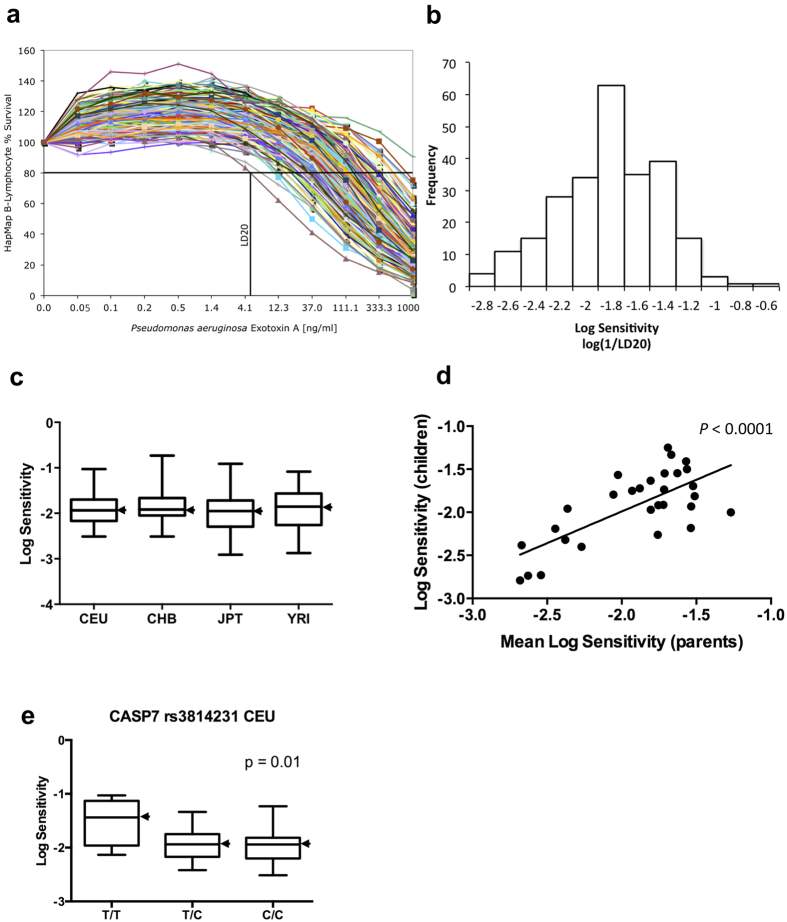
(a,b) Human lymphoblastoid cells sensitivity to P. aeruginosa exotoxin A (PE)-mediated toxicity. (a) 234 B-lymphocytes were treated with PE at concentrations shown. Cell viability was determined by Alamar Blue assay (Materials and Methods) and is shown as the percentage of survivors relative to cells treated with PE alone. The LD20 calculation for the most sensitive cell line is shown as an example. (b) LD20 values (ng/ml of PE) were calculated and expressed on an inverse log10 scale. For calculations, PE sensitivity is defined numerically as 1/LD20. (c) Population-specific distribution of toxins sensitivities. CEU, YRI, JPT, and CHB denote European, Yoruba, Japanese, and Chinese Han, respectively. One CHB outlier is excluded. For each population, the black bar represents the median log sensitivity; the box extends from the lower to the upper quartile and the whiskers extend to the most extreme data point. (d) Heritability of log sensitivity in Yoruba trios. Plot of the log toxin sensitivity of the children against the mean log toxin sensitivity of the parents. The heritability is estimated as the slope (0.74) of the regression of the children phenotype on the midparent phenotype. (e) In CEU caspase-7 SNP rs3814231 associates with log PE sensitivity.