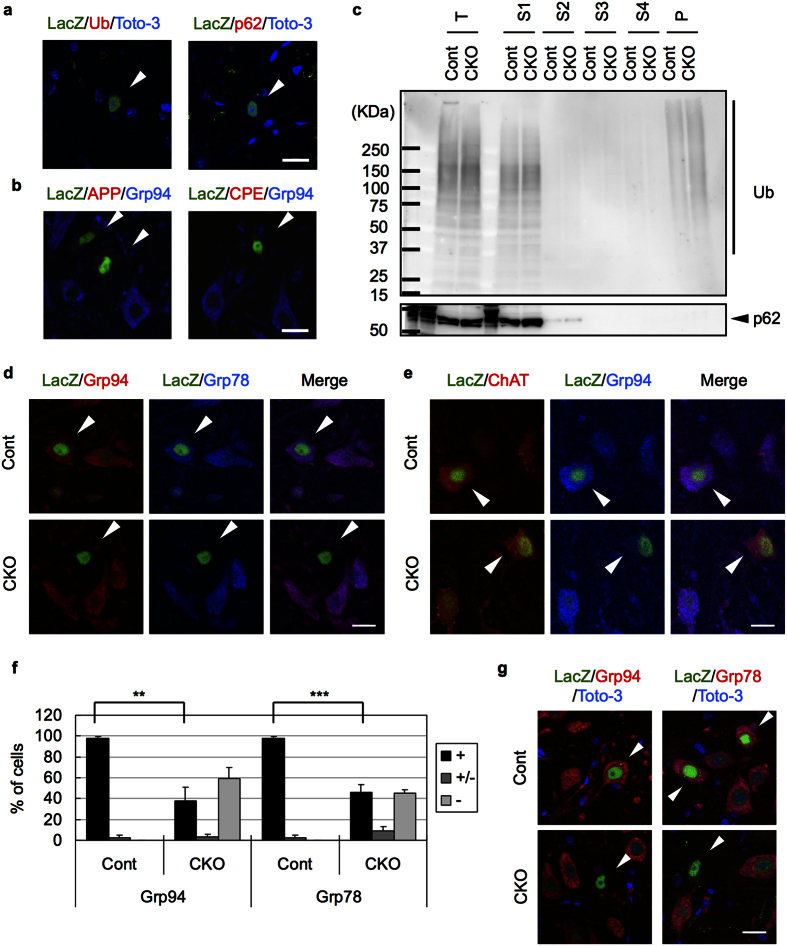
Figure 2. No accumulation of Ub/p62 and loss of ER chaperones in NF-YA v-cko motor neurons.
(a,b) Cervical cord sections of 6-week-old NF-YA v-cko mice (flox/flox; VA-cre; RNZ) were stained with LacZ together with indicated antibodies. Nuclei were stained with Toto-3 for (a). LacZ-positive cells are indicated by arrowheads. Note no accumulation of Ub, p62, APP or CPE in NF-YA v-cko motor neurons. (c) Isolated spinal cords from 14-week-old NF-YA v-cko mice (flox/flox; VA-cre) and control mice (flox/+) were homogenized (T), and then sequentially solubilized with buffer containing 1% TritonX-100 (S1), DNaseI/RNaseA (S2), 1% Sarkosyl (S3) or 4% Sarkosyl (S4), or with formic acid (P), and then analyzed by western blotting. Note no accumulation of insoluble Ub or p62 in NF-YA v-cko spinal cords. (d,e) Cervical cord sections of 6-week-old NF-YA v-cko (flox/flox; VA-cre; RNZ) or control (flox/+; VA-cre, RNZ) mice were stained with LacZ together with indicated antibodies. LacZ-positive cells are indicated by arrowheads. (d) Loss of both Grp94 and Grp78 in NF-YA v-cko neurons. (e) Remaining ChAT expression in the NF-YA v-cko neurons without Grp94 expression. (f) The LacZ-positive cells were categorized into three groups based on the staining of Grp94 or Grp78; no signal (−), background level (+/−) or similar to the control level (+). Ratios to total counted cells are shown. Values are means + s.d. of four mice data (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, t-test). (g) Facial nuclei of the mice used in a were stained with LacZ together with Grp94 or Grp78. Nuclei were stained with Toto-3. Loss of these ER chaperones in NF-YA v-cko facial motor neurons. Scale bars are 20 μm.