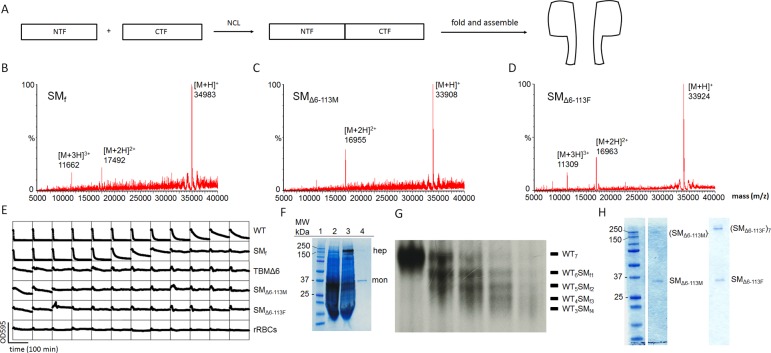
Figure 1.
Preparation of αHL pores. (A) αHL monomers were synthesized by native chemical ligation from two fragments (NTF and CTF) expressed in E. coli. Folding was performed by reducing the concentration of the denaturant (8 M urea) present during the purification of the synthetic monomers (SM). (B–D) Characterization of the synthetic αHL monomers by LC-MS. (B) SMf: [M + H]+ = 34 983 (observed mass, obs), 34 981 (calculated mass, calcd). (C) SMΔ6-113M: [M + H]+ = 33 908 (obs), 33 907 (calcd). (D) SMΔ6-113F: [M + H]+ = 33 924 (obs), 33 923 (calcd). (E) Hemolysis assays (see Supporting Information, Experimental procedures). The decrease in light scattering over time was recorded in a microplate reader at 595 nm. WT αHL monomer (row 1) lysed rRBCs, whereas TBMΔ6 (row 3) did not due to its truncated β barrel. Similarly, the full-length synthetic αHL monomer SMf (5.9 μg mL–1, in well 1) lysed rRBCs, whereas SMΔ6–113M (7.4 μg mL–1) and SMΔ6–113F (7.8 μg mL–1) did not. WT and TBMΔ6 monomers were produced by IVTT. (F) SDS-PAGE gel analysis of WT and synthetic αHL (SMf). Lane 1: molecular markers. Lane 2: radiolabeled αHL monomer (mon) produced by IVTT. Lane 3: radiolabeled WT7 pores (hep) produced in the presence of DPhPC liposomes (7 mg mL–1). Lane 4: (SMf)7 pores assembled with purified SMf in the presence of DPhPC liposomes under the same conditions comigrate with the WT7 pore. An autoradiogram is superimposed on the Coomassie Blue-stained gel. (G) Heteroheptameric pores. WT αHL (radiolabeled protein) and SM were mixed in various ratios in the presence of rRBCm to yield heteromeric WT7–nSMn (n = 0–7) pores. The heptameric pores with different numbers of SMf were separated by SDS-PAGE based on the different electrophoretic mobilities produced by D8 tails at the C-terminus of SMf. (H) Homoheptameric pores formed with SMΔ6–113M (left) and SMΔ6–113F (right). Homomeric pores were prepared in the presence of DPhPC liposomes (10 mg mL–1).