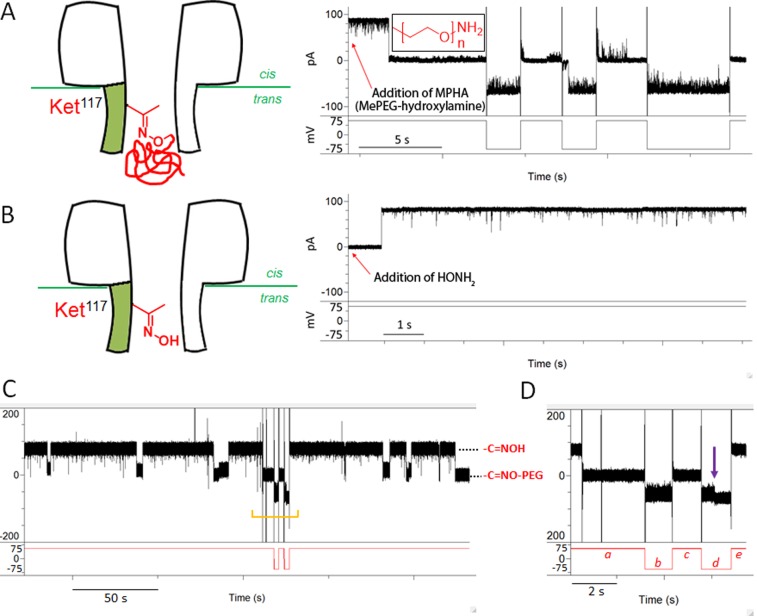
Figure 4.
Single-molecule reactions of the WT6SMket1 pore. (A) A WT6SMket1 pore was reacted with MePEG-hydroxylamine (MPHA, 1.1 kDa, 2 mM, inset) added to the trans compartment. Reaction occurred at a positive potential (+75 mV) and led to a permanent current blockade of the WT6SMket1 pore. The modified pore only opened at negative applied potentials. (B) The pore was restored to an open state when 20 mM HONH2·HCl was added to both compartments to release the PEG chain. The currents in (A) and (B) were filtered at 5 kHz and sampled at 25 kHz. For display, further digital filtering was carried out at 2 kHz with an 8-pole low-pass Bessel filter. The buffer was 1 M KCl, 50 mM Na acetate (pH 3.4). (C) Reversible oxime formation in a single synthetic pore containing a ketone (WT6SMket1). Oxime formation with MPHA leads to a current drop, while reversal with HONH2 returns the current to its initial level. The section defined by the orange bracket is magnified in panel D. (D) Negative potential (−75 mV, b) was applied during the PEG-oxime state (a), which opened the pore (residual current, IRES = 91%). Subsequently, a positive potential (+75 mV, c) was applied, and the pore closed. The pore became fully open (violet arrow) with IRES = 100% at negative potential (−75 mV, d), presumably when the formation of an oxime with HONH2 led to release of the pore-bound polymer. The pore was restored to an open state at a positive potential (+75 mV, e).