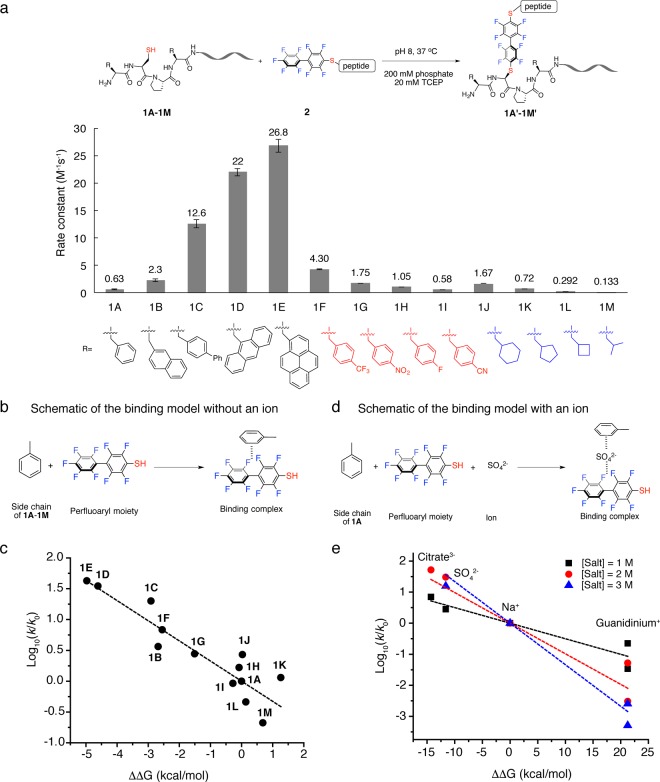
Figure 5.
Mutation and computational studies on salt effect and π-clamp mediated arylation. (a) Rate constants for reactions between π-clamp mutants and perfluoroaryl probe 2. Reaction conditions: 200 mM phosphate, 20 mM TCEP, pH 8.0, 37 °C. (See Figures S28–S40 for detailed conditions of each reaction.) (b) Schematic of the binding model used for calculating the binding energy without an ion. (c) Linear free energy relationship (LFER) between the experimental reaction rate constant (k) and computational binding energy relative to baseline (ΔΔG, defined as ΔG – ΔG0). log10(k/k0) was found linearly correlated with ΔΔG. To serve as baseline, the term k0 refers to the rate constant of arylation reaction between peptide 1A and probe 2 without additional salt, and ΔG0 refers to the calculated binding energy in the binding model for 1A without an ion. (d) Schematic of the binding model used for calculating the binding energy with an ion. (e) Linear free energy relationship (LFER) between the experimental reaction rate constant (k) and computational binding energy with an ion incorporated relative to baseline (ΔΔG, defined as ΔG – ΔG0). log10(k/k0) was found linearly correlated with ΔΔG. The term k0 refers to the rate constant of the arylation reaction between 1A and 2 with NaCl, and ΔG0 refers to the calculated binding energy with Na+ incorporated in the binding model for 1A.