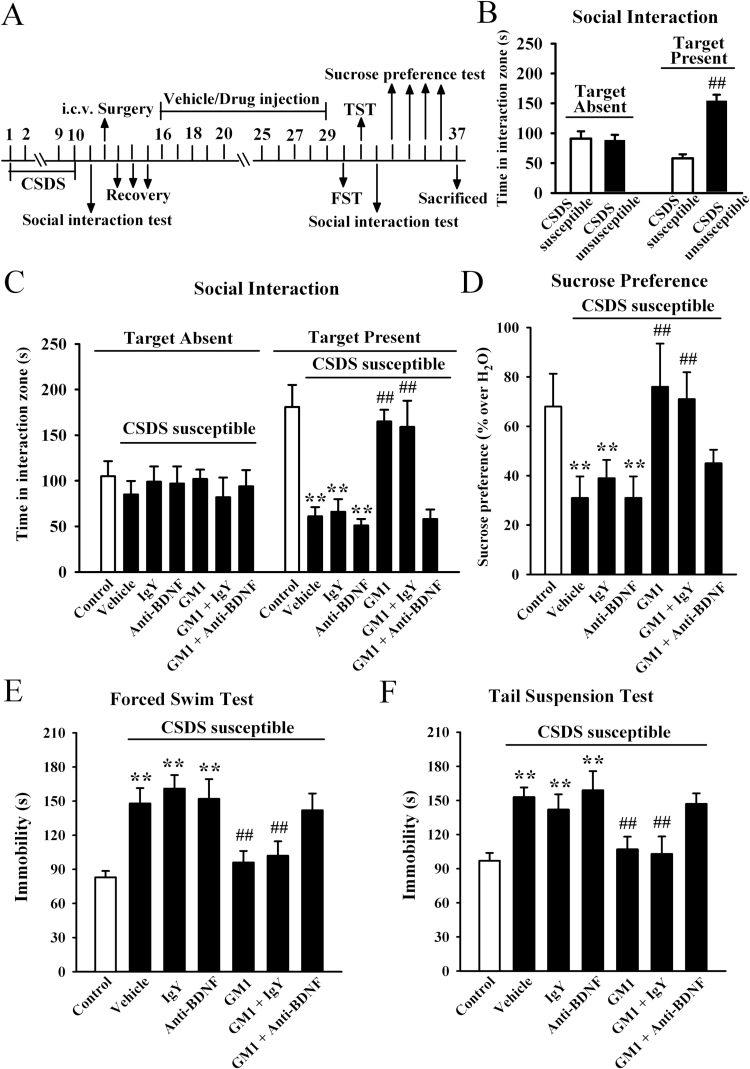
Figure 5.
Blockade of brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) signaling cascade by anti-BDNF infusion abolishes the antidepressant-like effects of monosialotetrahexosylganglioside (GM1). (A) Schematic timeline of the experimental procedure. Total 103 C57BL/6J mice were used in this experiment with 92 chronic social defeat stress (CSDS)-stressed mice and 11 nonstressed mice. CSDS-susceptible mice were co-treated with GM1 and anti-BDNF antibody for 14 days, with behavioral tests then performed. The vehicle refers to 0.9% saline. (B) The social interaction results for CSDS-susceptible mice (n = 63) and unsusceptible mice (n = 29) in this experiment. (C) Co-treatment with GM1 and anti-BDNF blocked the antidepressant-like effects of GM1 in the social interaction test. CSDS-susceptible +GM1+anti-BDNF mice displayed significantly lower social interaction than CSDS-susceptible+GM1 mice (n=10–11). (D) SDS-susceptible+GM1+anti-BDNF mice displayed significantly lower sucrose preference than CSDS-susceptible+GM1 mice (n=10–11). (E) CSDS-susceptible + GM1+anti-BDNF mice displayed significantly higher immobility time than CSDS-susceptible + GM1 mice in the forced swim test (FST) (n = 10–11). (F) CSDS-susceptible + GM1 + anti-BDNF mice also displayed significantly higher immobility time than CSDS susceptible + GM1 mice in the tail suspension test (TST) (n = 10–11). Results are expressed as the mean ± SEM; ** P<.01 vs control; ## P<.01 vs CSDS-susceptible/CSDS-susceptible + vehicle. Comparison was made by 2-way ANOVA followed by posthoc Bonferroni’s test