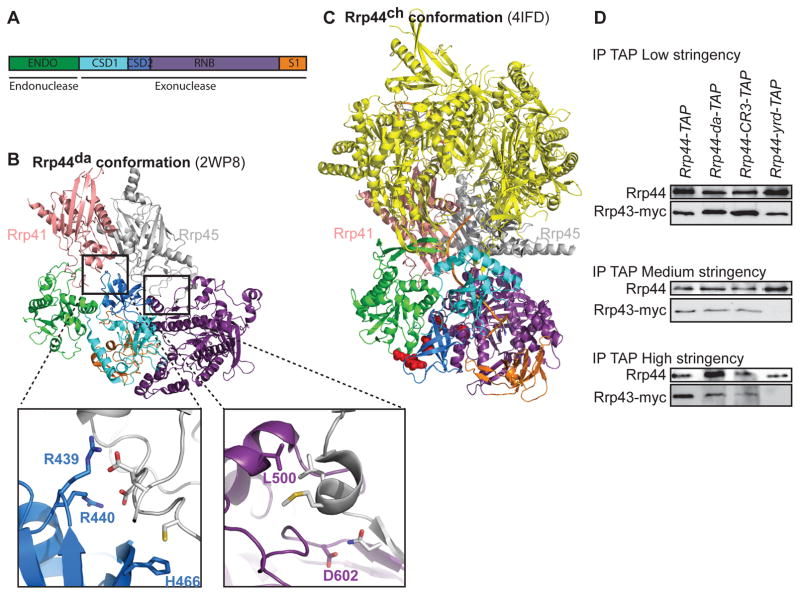
Figure 1. Identification of residues important for the direct access conformation of the RNA exosome.
(A) Domain organization of Rrp44. ENDO: endonuclease domain; CSD1/2: Cold Shock Domain 1/2; RNB: RNase II family catalytic domain; S1: S1 RNA Binding Domain. The domains are color coded as in panels B and C (B) Five conserved residues (R439, R440, H466, L500, and D602) that are important for the formation of the Rrp44da-conformation. (C) The five residues (shown as red spheres) are located on the bottom and exposed to solvent in the Rrp44ch-conformation. Cartoon versions of the X-ray crystal structures were generated by MacPyMol (Schrödinger, LLC). (D) Mutations in the five resides of panel B disrupt the Rrp44-exosome interaction. TAP-tagged variants of Rrp44 were immunoprecipitated at different wash conditions, and western blot was conducted by using α-Protein A and α-Myc antibodies.