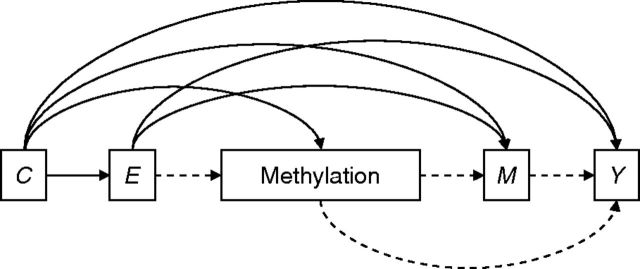
Figure 1.
“Early programming” model, Jerusalem Perinatal Family Follow-up Study, 1974–2009. Methylation is established in early life. Under this hypothesized causal structure, a woman's methylation status is established early in life by birth socioeconomic position ( E ) and perinatal characteristics ( C ) and is independent of subsequent life-course mediators ( M ) such as childhood overweight, attained education, marital status, religiosity, childbearing, or substance use. The mediated effect of E on adult phenotype ( Y ) through methylation status (i.e., the indirect effect) is given by the dashed lines, and M need not be controlled for in examining exposure-methylation associations.