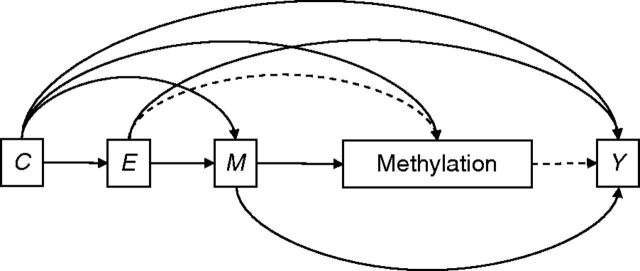
Figure 2.
“Cumulative effects” model, Jerusalem Perinatal Family Follow-up Study, 1974–2009. Methylation is affected by life-course mediators. Under this hypothesized causal structure, an adult woman's methylation status is determined by birth socioeconomic position ( E ), perinatal characteristics ( C ), and life-course mediators ( M ). One possible mediated effect of E on adult phenotype ( Y ) is given by the dashed lines. We are interested in the dashed paths, so M should be adjusted for in analyses. Note that adolescent overweight (a component of M ) may be an important biological pathway for early life development, so we adjust for it indirectly through weighting.