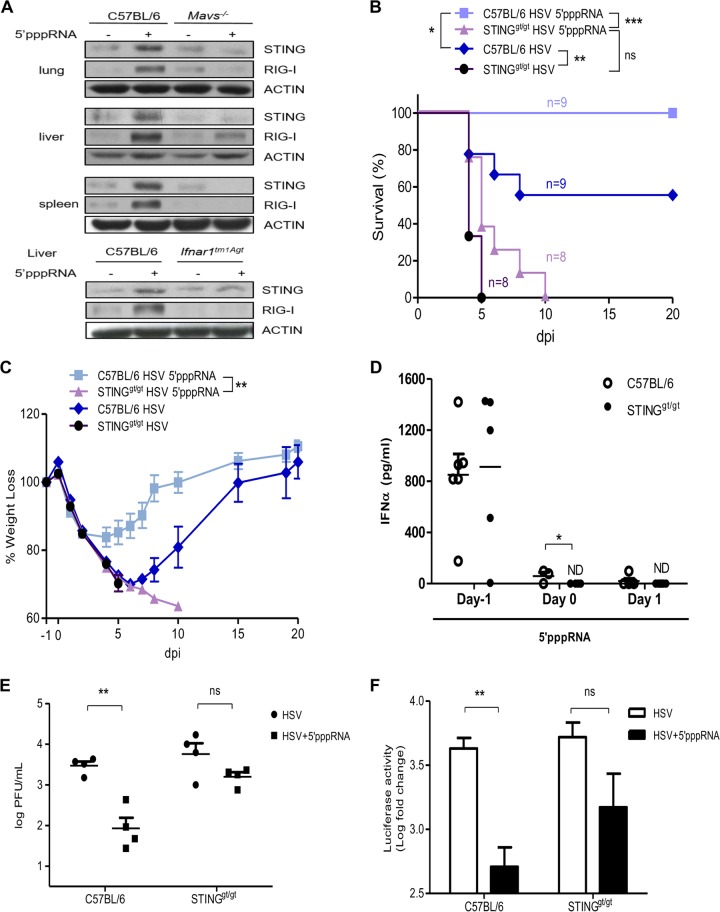
FIG 7.
STING is essential for 5′pppRNA-mediated protection from HSV-1 infection in vivo. (A) Six-week-old C57BL/6J mice, Mavs−/− mice, or Ifnar−/− mice were injected intravenously with 25 μg of 5′pppRNA in complex with in vivo-jetPEI. Immunoblot analyses were performed to measure the levels of STING, RIG-I, and actin protein expression in the indicated organs at 24 h posttreatment. (B to D) C57BL/6 mice and STINGgt/gt mice were treated with 5′pppRNA on the day prior to lethal HSV-1–Luc infection (2 × 107 PFU, day −1) and the day of infection (day 0). Percent survival (B) and percent weight loss (C) were monitored. (D) Serum IFN-α was quantified by ELISA. ND, not detectable. (E, F) C57BL/6 mice and STINGgt/gt mice were treated with 5′pppRNA on the day prior to nonlethal HSV-1–Luc infection (1 × 106 PFU, day −1) and the day of infection (day 0). Lung viral titers (E) and viral luciferase activity (F) in lung were measured on day 3 postinfection. Error bars represent SEMs of the results for four different animals. Statistical analysis was performed by Student's test, log-rank tests, or two-way analysis of variance (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ns, not statistically significant).