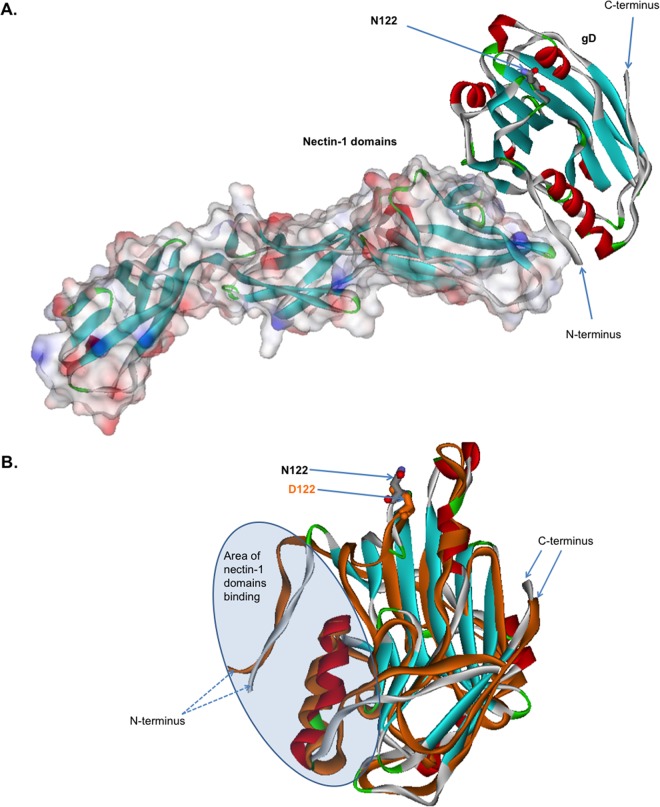
FIG 5.
Computational modeling and comparison of the structures of B virus gD-122N and gD-122D variants liganded with nectin-1. (A) Computational modeling of B virus N122-carrying gD and nectin-1. The solved crystal structure of HSV-1 gD bound to human nectin-1 (PDB code 3U82) was used as a template. B virus gD and nectin-1 are represented as a stereo ribbon and van der Waals surfaces, respectively. The N122 residue is located more than 15 Å from the protein-protein nectin-1–gD interface and thus is not involved in the direct interaction between gD and nectin-1. (B) Overlay of the B virus gD-122N and gD-122D structures. The arrows mark N122 (gray) and D122 (orange). Note the considerable conformational changes of the globule in the area of the nectin-1 binding domain. These changes lead to a reduction in the energy of binding of the gD-122D variant to nectin-1, by ∼0.16 kcal/mol, compared to that of the gD-122N variant.