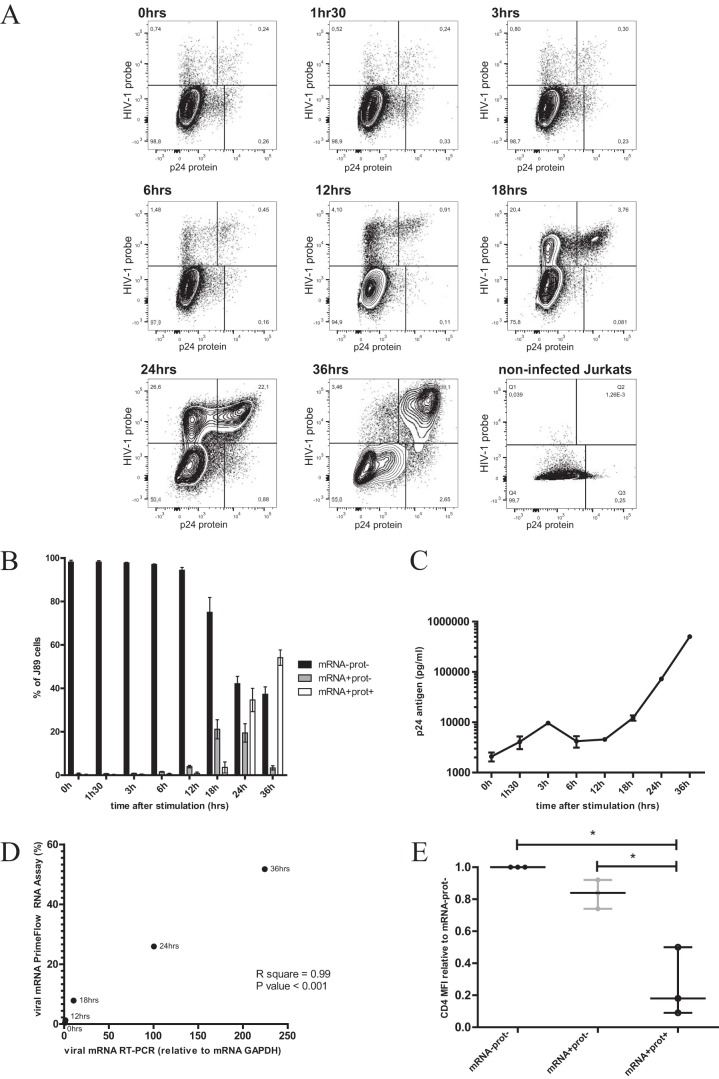
FIG 3.
RMD stimulation of J89 cells. J89 cells were activated with RMD (5 nM) at time points ranging from 1 h 30 min to 36 h. A PrimeFlow RNA assay was performed at the indicated time points following stimulation. (A) Representative data showing the kinetics of the viral mRNA-single-positive population, the viral mRNA/protein-double-positive population, and the viral protein-single-positive population. (B) Analysis of viral mRNA and viral protein production over time in J89 cells stimulated with RMD (5 nM) in three independent replicates. The double-negative population decreased over time with stimulation, while at 6 h, the single-positive viral mRNA population already started to be detectable, reaching its peak at 18 h to 24 h poststimulation and decreasing by 36 h poststimulation. The viral mRNA/protein-double-positive population was first measurable at 12 h poststimulation and increased up to maximum levels of 56% (as a mean) at 36 h poststimulation. Uninfected Jurkat cells were included as a control. (C) Measurement of p24 antigen levels in supernatants of stimulated J89 cells with a p24 ELISA (Bio-Rad). Unstimulated cells were used as a background control (0 h). Experiments were performed in triplicates, and the horizontal bars are representative of medians ± standard deviations. (D) Parallel measurement of viral mRNA by real-time PCR and a PrimeFlow RNA assay on stimulated J89 cells at the indicated time points showed a statistically significant correlation (R2 = 0.99; P < 0.001). (E) CD4 expression in J89 cells was measured at 24 h poststimulation (n = 3), after RMD treatment (5 nM). Data evaluated with a Wilcoxon signed-rank test indicated that CD4 levels were already downregulated at the viral mRNA+ stage (P < 0.005), and CD4 downregulation increased with increasing viral protein production (P < 0.05).