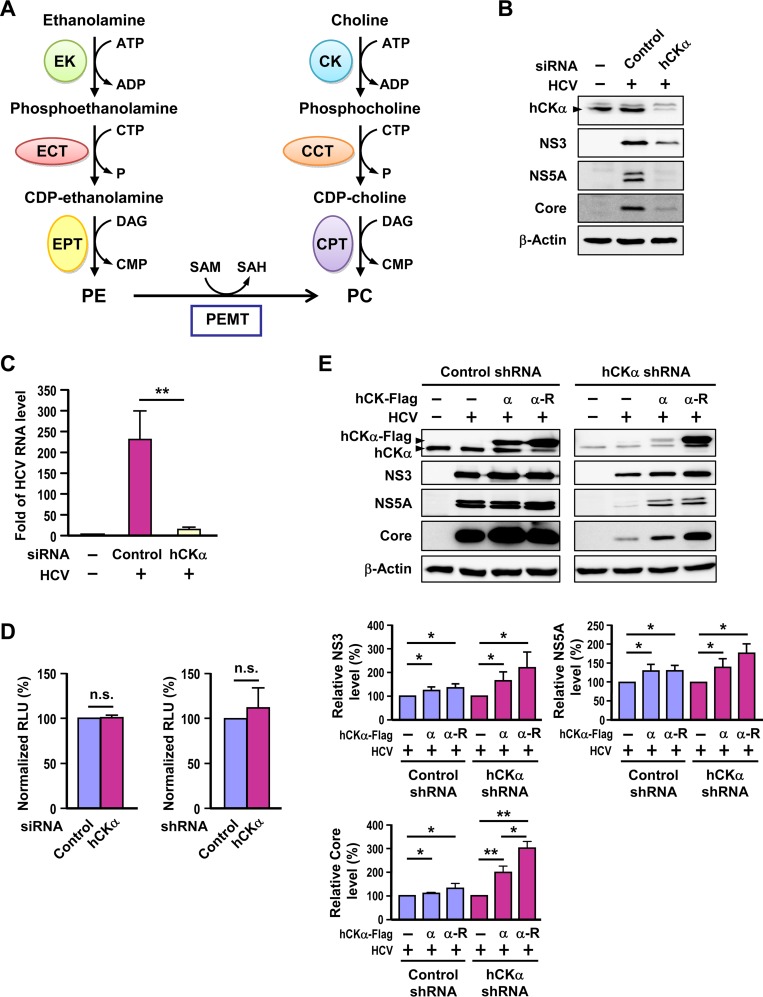
FIG 1.
Involvement of hCKα in HCV replication. (A) Biosynthesis of phosphatidylcholine (PC) and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE). PC is mainly synthesized via the CDP-choline and PE methyltransferase (PEMT) pathways. In the CDP-choline pathway, choline kinase (CK), CTP:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase (CCT), and choline phosphotransferase (CPT) catalyze consecutive reactions to produce PC. In the PEMT pathway, PE undergoes three methylation reactions catalyzed by PEMT to synthesize PC. In the CDP-ethanolamine pathway, ethanolamine is taken up into the cytoplasm and catalyzed by ethanolamine kinase (EK), CTP:phosphoethanolamine cytidylyltransferase (ECT), and ethanolamine phosphotransferase (EPT) to yield PE. (B and C) Huh7 cells remained untransfected (−) or were transfected with an untargeted control siRNA or hCKα-specific siRNA. Cells were then infected with HCVcc at an MOI of 1 or received parallel treatment without HCVcc (−). Cells were then subjected to Western blot analysis (B) and RT-PCR (C). (D) Huh7 cells transfected with control or hCKα siRNAs (left panel) and Huh7 cells stably transduced with control or hCKα shRNA lentiviral vectors (right panel) were assessed for cell viability. (E) The control and hCKα shRNA Huh7 stable cells were transfected with plasmids encoding the Flag-tagged normal hCKα (α) or shRNA-resistant hCKα (α-R) followed by infection with HCV. The cells were analyzed by Western blotting (top panel). The levels of NS3, NS5A, and core proteins in HCV-infected control or hCKα stable knockdown cells overexpressing hCKα or hCKα-R are expressed as a percentage relative to that detected in vector plasmid transfected cells, which was designated 100% (bottom panel). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ns, nonsignificant.