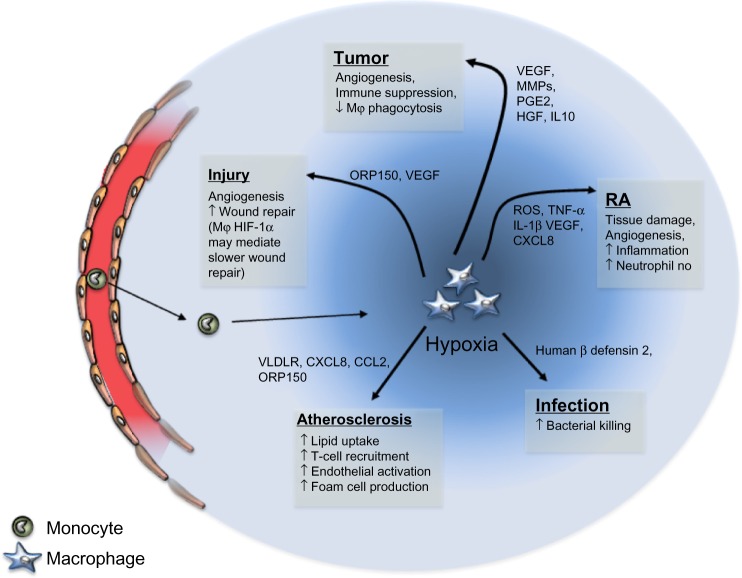
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the role of macrophages following exposure to hypoxia in varying disease states.
Notes: Macrophages are recruited as monocytes from circulation. They enter the hypoxic environment of the diseased tissue and upregulate cytokines/proteases (black arrows) that mediate downstream biological functions (gray boxes) in each disease state. The up arrows correspond to an increase in expression or activity; the down arrows correspond to a downregulation in expression or activity.
Abbreviations: VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; IL10, interleukin 10; ORP150, oxygen-regulated protein 150; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL-1β, interleukin 1 beta; VLDLR, very low-density lipoprotein receptor; CCL2, chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2; HIF-1, hypoxia-inducible factor-1; Mϕ, macrophage; ORP150, oxygen-regulated protein 150; RA, rheumatoid arthritis.