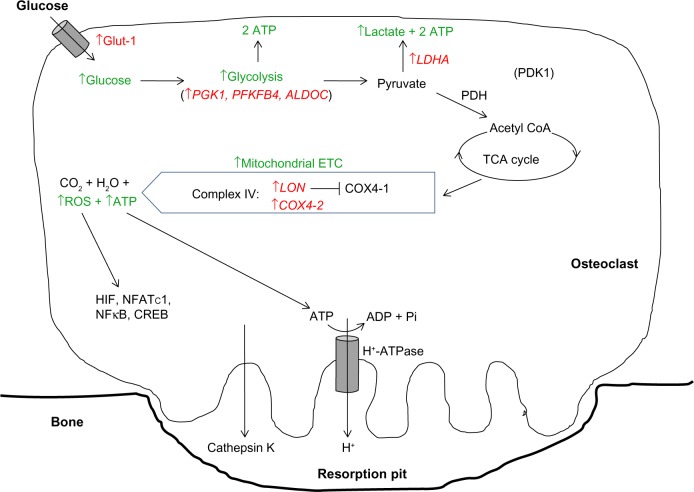
Figure 2.
Modification of the HIF-mediated switch to anaerobic respiration in osteoclasts.
Notes: Osteoclasts specifically increase flux through both the glycolytic pathway and mitochondrial ETC to provide ATP and ROS necessary for bone resorption. HIF-regulated genes are shown in red. Green type indicates downstream effects of modulation of HIF target genes.
Abbreviations: Glut-1, glucose transporter 1; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; PGK1, phosphoglycerate kinase 1; PFKFB4, 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2, 6-biphosphatase 4; ALDOC, aldolase C; LDHA, lactate dehydrogenase A; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; PDK1, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1; TCA, tricarboxylic acid; COX4-1/2, cytochrome c oxidase subunit 4 isoform 1/2; ETC, electron transport chain; ROS, reactive oxygen species; HIF, hypoxia-inducible factor; NFκB, nuclear factor kappa B; NFATc1, nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic, calcineurin-dependent 1; CREB, cAMP response element-binding protein; LON, lon protease homologue, mitochondrial; ADP, adenosine diphosphate; coA, co-enzyme A.