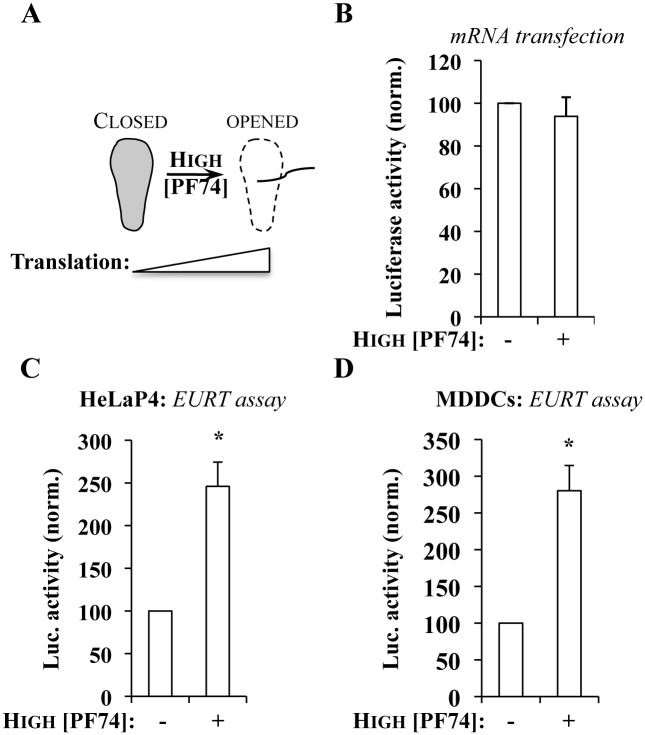
Fig 4. At high concentrations, the HIV-1 core-destabilizing compound PF74 induces an increase in Luciferase activity measured upon EURT assay.
A) Due to its well described destabilizing effect on viral cores, PF74 is expected at doses superior to 10 μM to increase the availability of EU-repRNA to the translation machinery. B) To exclude pleiotropic effects of PF74 on translation, HeLaP4 cells were transfected with an in vitro synthesized, capped mRNA coding F-Luc in the presence or absence of PF74 (at 10 μg/mL, which corresponds to 23 μM). Luciferase accumulation was measured 8 hours afterwards. C and D) HeLa P4 or MDDCs were challenged with HIV-1 virus, bearing either an X4- or an R5-tropic Env and incorporating EU-repRNA (MOI equivalent of 0.5, after exo-RT normalization against standards of known infectious titer) in the presence or absence of PF74 (as above), prior to cell lysis and Luciferase activity measurement. Averages and SEM of 6 independent experiments are presented (with cells obtained from different donors in the case of MDDCs). *statistically significant differences following a Student t test (p≤0.05).