Fig 3. Selectivity index for different nonlinearities f.
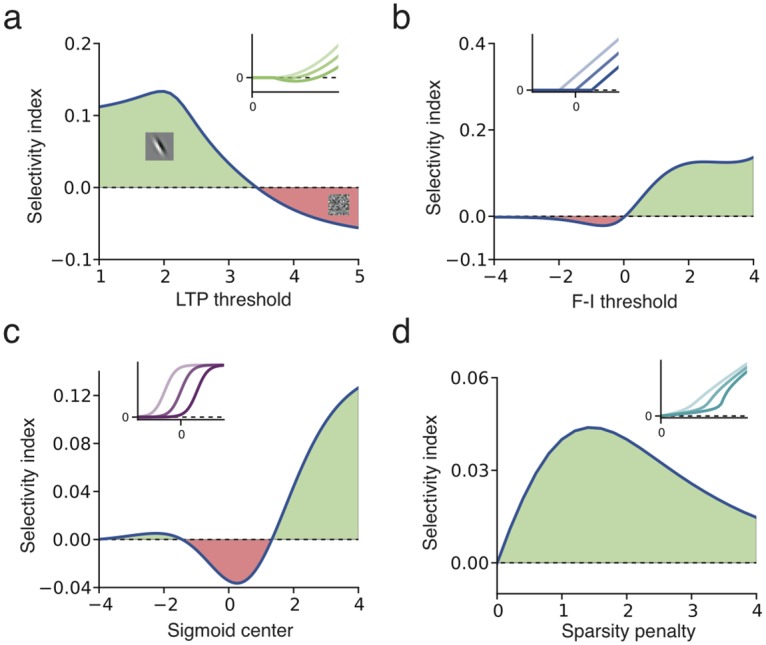
(a) Quadratic rectifier (small graphic, three examples with different LTP thresholds) with LTD threshold at θ1 = 1: LTP threshold must be below 3.5 to secure positive selectivity index (green region, main Fig) and learn localized oriented receptive fields (inset). A negative selectivity index (red region) leads to a random connectivity pattern (inset) (b) Linear rectifier: activation threshold must be above zero. (c) Sigmoid: center must be below a = − 1.2 or, for a stronger effect, above a = +1.2. The opposite conditions apply to the negative sigmoid. (d) Cauchy sparse coding nonlinearity: positive but weak feature selectivity for any sparseness penalty λ > 0. Insets show the nonlinearities for different choices of parameters.
