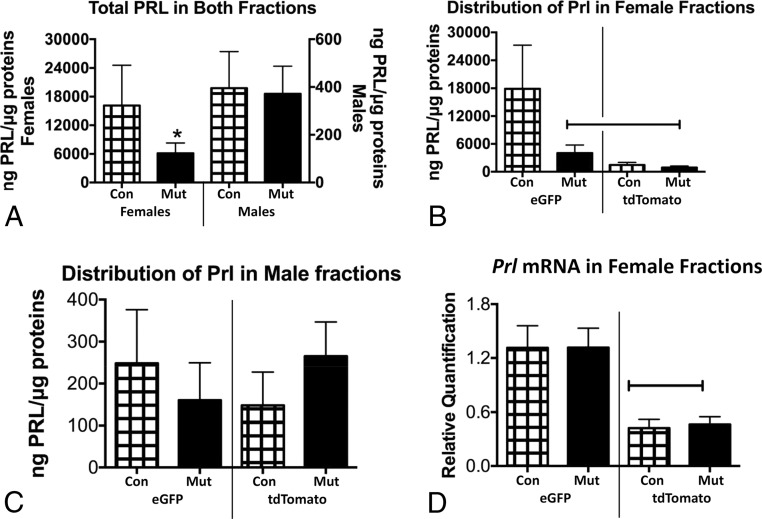
Figure 7.
A, EIAs of total PRL show significant sex difference in overall levels, comparing females (left, y-axis) with males (right, y-axis) and an overall reduction of PRL only in somatotrope Lepr-null females. *, Lowest value by ANOVA/Newman-Keuls (P = .04; n = 4–5). B, Distribution of Prl across eGFP and tdTomato fractions shows that eGFP fractions from control females have significantly more Prl than tdTomato fractions. Mutant eGFP fractions store significantly less Prl, however. Capped line, Lowest values by ANOVA/Newman-Keuls (P = .038; n = 4–5). C, Distribution of Prl in male fractions shows no differences between controls and mutants or between eGFP and tdTomato fractions (ANOVA, P = .75). D, Distribution of Prl mRNA in female fractions shows that eGFP fractions from mutants have the highest levels compared with tdTomato fractions. There are no differences between controls and mutants for either fraction. Capped line, Lowest values by ANOVA/Newman-Keuls (P = .0002; n = 4–5). Con, control; Mut, somatotrope Lepr-null mutant.