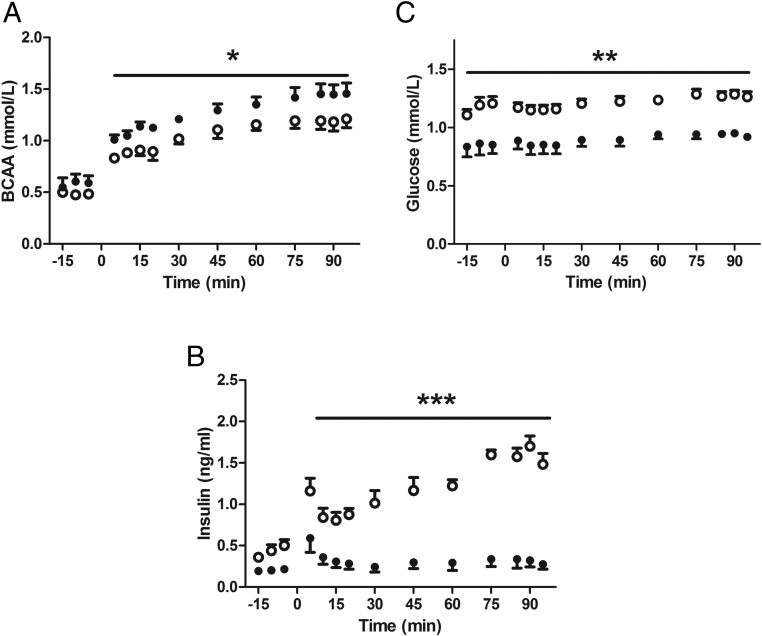
Figure 1.
IUGR fetuses have attenuated acute in vivo AASIS. CON (open circles, n = 5) and IUGR (closed circles, n = 5) underwent a primed, continuous, constant-rate hyperaminoacidemic clamp with a direct fetal infusion of 10% TrophAmine (wt/vol) starting at time 0. A, BCAA concentrations increased in both groups and were higher in the IUGR fetuses compared with CONs (*, P < .05). B, IUGR fetuses had significantly lower fetal arterial plasma insulin concentrations during the clamp (***, P < .0001). C, Fetal arterial plasma glucose concentrations increased slightly in both groups (P < .005) but were consistently lower in the IUGR-SAL fetuses (**, P < .0001). Mean ± SE fetal arterial plasma concentrations are plotted and statistics are by mixed models ANOVA.