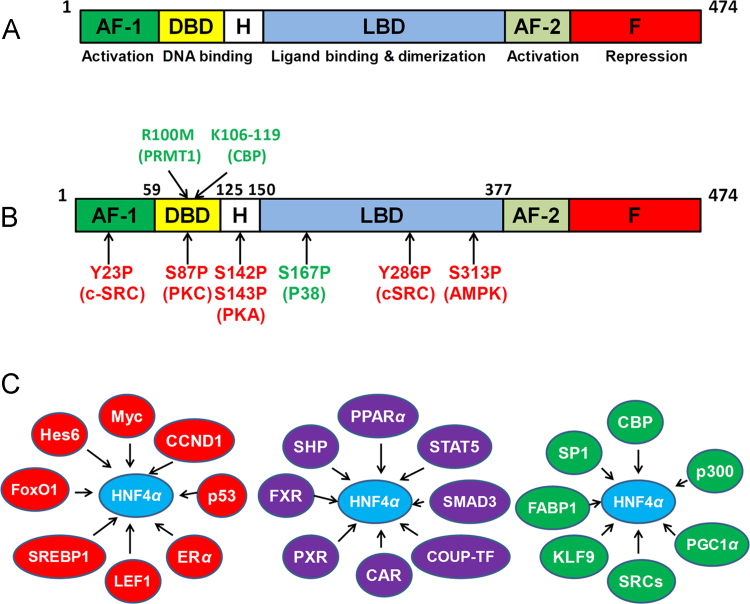
Figure 1.
Diagrams that illustrate the protein domain structure (A), posttranslational modifications (B), and interactions (C) of HNF4α with other signaling pathways. (A) Domain structure of HNF4α protein, with the 474-amino-acid-long human HNF4α2 shown as the canonical HNF4α isoform. (B) Posttranslational modifications of HNF4α. HNF4α is methylated at arginine 100 (R100M) by PRMT1, and acetylated at lysines 106, 108, 118, or 119 by CBP. HNF4α is phosphorylated at lysine-23 (Y23P) and Y286 (Y286P) by c-SRC, serine 87 (S87P) by PKC, serine 142 and 143 (S142P and S143P) by PKA, serine 167 (S167P) by P38, and serine 313 (S313P) by AMPK. The positions of post-translational modifications of HNF4α have been renumbered in the text and Fig. 1 based on the updated NCBI protein database for HNF4α2 (NP_000448.3), which is also used as the canonical protein isoform for human HNF4α in PhosphoSitePlus®, a public database for posttranslational modifications of proteins43. (C) Transcriptional factors that modulate the transcriptional activity of HNF4α through physical interactions. Red shape: negative interaction; purple shape: both negative and positive interactions; green shape: positive interaction.