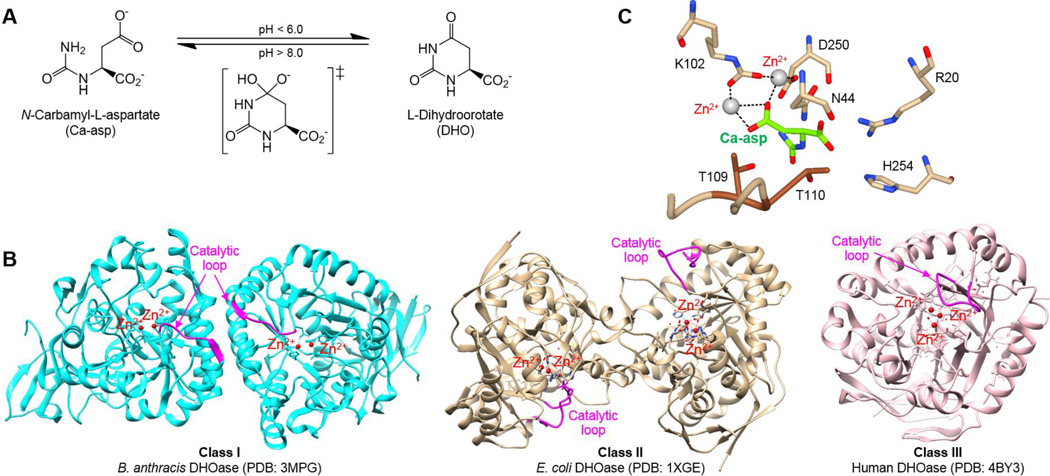
Figure 1. The mechanism of DHOase.
(A) The enzyme catalyzes the reversible cyclization of Ca-asp to DHO. (B) Ca-asp is stabilized by the Zn2+ ions coordinated by a carboxylated K102, while D250 abstracts the proton from the amide nitrogen of Ca-asp. (PDB: 1XGE). The exocyclic carboxyl group of Ca-asp is stabilized by N44, R20, and H254, in addition to the T109 and T110 from the ‘in’ formation of the catalytic loop. (C) Comparison of the three classes of DHOase with the catalytic loop highlighted in pink.