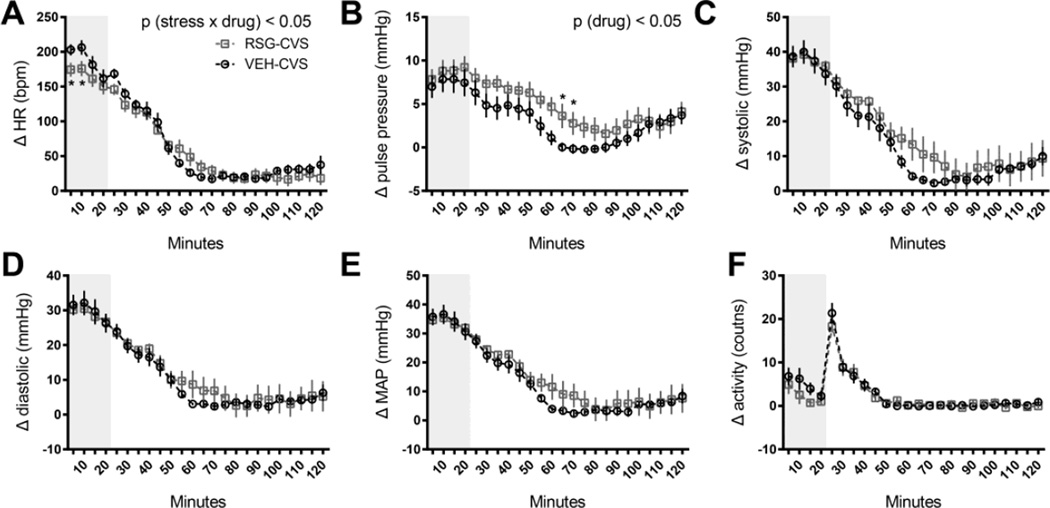
Figure 1. Rosiglitazone (RSG) and the cardiovascular response to acute stress.
Rats treated with oral RSG (10 mg/kg body weight, once daily) exhibited a significantly blunted heart rate (A), and a significantly elevated pulse pressure (B) response to a 20-minute restraint challenge (represented by gray shading), compared to rats treated with vehicle alone (VEH). There were no significant effects of RSG on the systolic (C), diastolic (D), mean arterial (MAP) pressure (E) or locomotor (F) response to this acute stressor. Data are represented as means of 5 minute time bins ±SEM for 120 minutes during and immediately following restraint. * p<0.05 by Tukey’s posthoc test; n =8 rats per group.