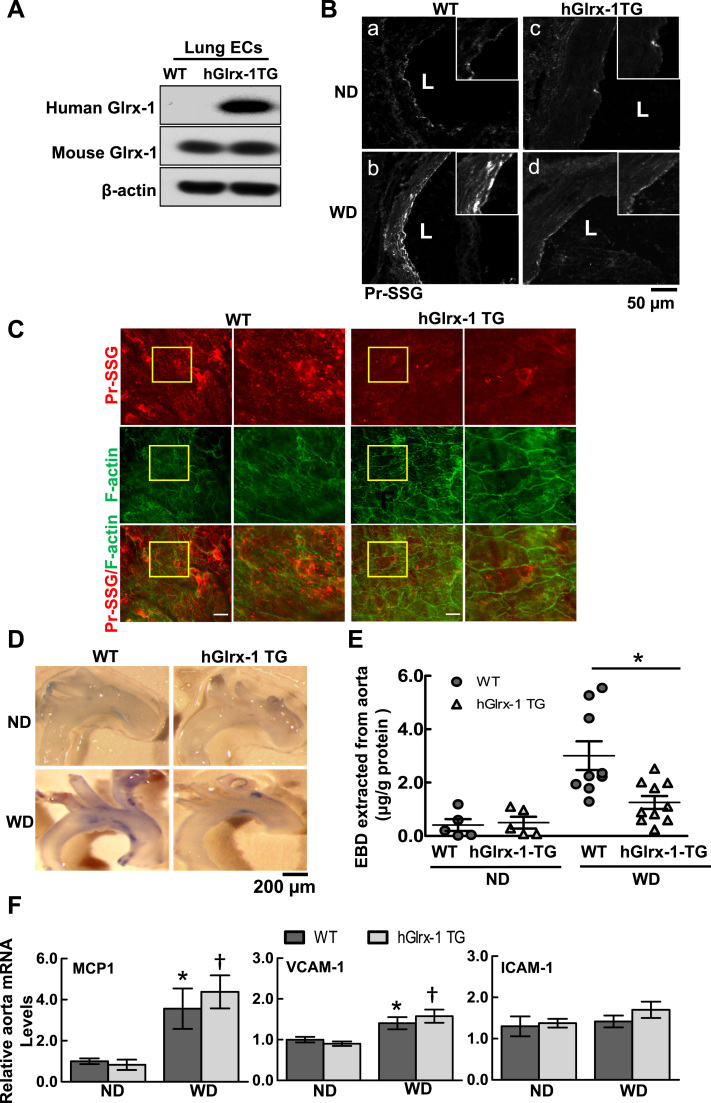
Fig. 3.
Transgenic overexpression of human Glrx-1 in ApoE-/- mice attenuates hypercholesterolemia-induced protein S-glutathionylation and aortic barrier dysfunction in vivo. A. ECs isolated from the lung of human Glrx-1 transgenic (hGlrx-1 TG) mice express human Glrx-1. B-C: hypercholesterolemia-induced PrS-SG is diminished in aortic endothelium of hGlrx-1 TG mice, accompanied by preserved EC actin cytoskeletal structure. WT and hGlrx-1 TG mice on ApoE-/- background were fed ND or WD for 2 weeks. B: Representative immunofluorescence images show PrS-SG staining in aortic cross-sections from WT and hGlrx-1 TG. Inserts are high magnification views of yellow boxed areas. Scale bar is 50 µm. C: Representative en face confocal fluorescence images of PrS-SG (red channel) and cytoskeletal organization (F-actin, green channel) in aortic endothelium at the lesser curvature of aortic arch segments from WT and hGlrx-1 TG mice. The second and last column show high magnification view of yellow box areas. Scale bars are 20 µm. D–E: Hypercholesterolemia-induced aortic permeability is attenuated in hGlrx-1 TG mice. Aortic permeability in WT and hGlrx-1 TG mice on ND and WD was assessed by BSA-Evans blue dye (BSA-EBD) conjugate permeation method. F: Representative photographs of BSA-EBD leakage in aortic arch segments of mice. Scale bar is 200 µm. G: The permeated EBD in aortae was extracted, measured, and presented as means±SEM (WT: n=5–9; hGlrx-1 TG: 5–10). *p<0.05 between indicated groups. H: Hypercholesterolemia-induced inflammatory genes including MCP1, VCAM1, and ICAM1, in aorta is not affected by overexpression of hGlrx-1. Bar graphs show normalized mRNA level of inflammatory genes relative to ND group. Data are represented as mean±SEM. WT on ND (n=5) and WD (n=5). hGlrx-1 TG on ND (n=5) and WD (n=7). *p<0.05 vs. WT mice on ND group, † p<0.05 vs. hGlrx-1 TG mice on ND group. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)