Figure 1.
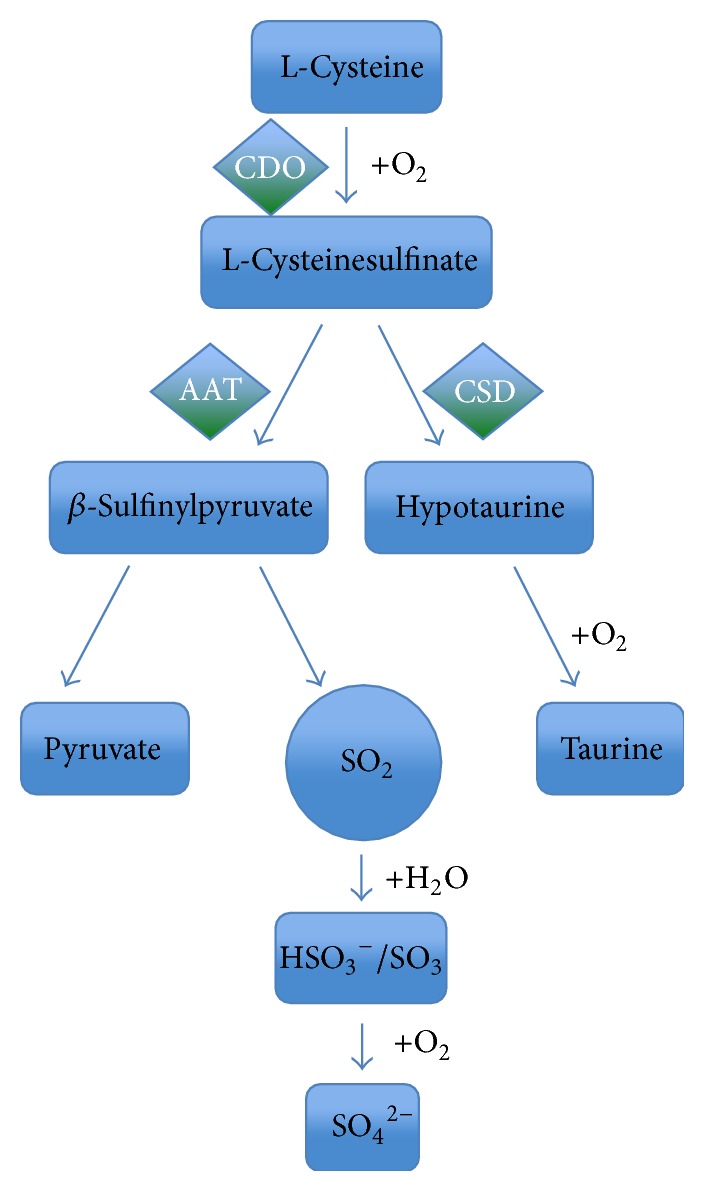
Endogenous generation of sulfur dioxide. Firstly, a sulfur-containing amino acid is metabolized to L-cysteine that is then oxidated into L-cysteinesulfinate under the role of CDO. L-Cysteinesulfinate, an analogue of L-asparaginic acid, can be transaminated into β-sulfinylpyruvate under the role of AAT, which is spontaneously decomposed into pyruvate and SO2. In vivo, SO2 can produce HSO3 −/SO3 2− (molar ratio of 1 : 3) after combining with water, which can be oxidated into SO4 2− by sulfite oxidase and then excreted through the kidneys. On the other hand, L-cysteinesulfinate can be also decarboxylated into CO2 and hypotaurine under the role of CSD. A large majority of hypotaurine can be further oxidized into taurine. SO2: sulfur dioxide; CDO: cysteine dioxygenase; CSD: cysteinesulfinate decarboxylase; AAT: aspartate aminotransferase.
