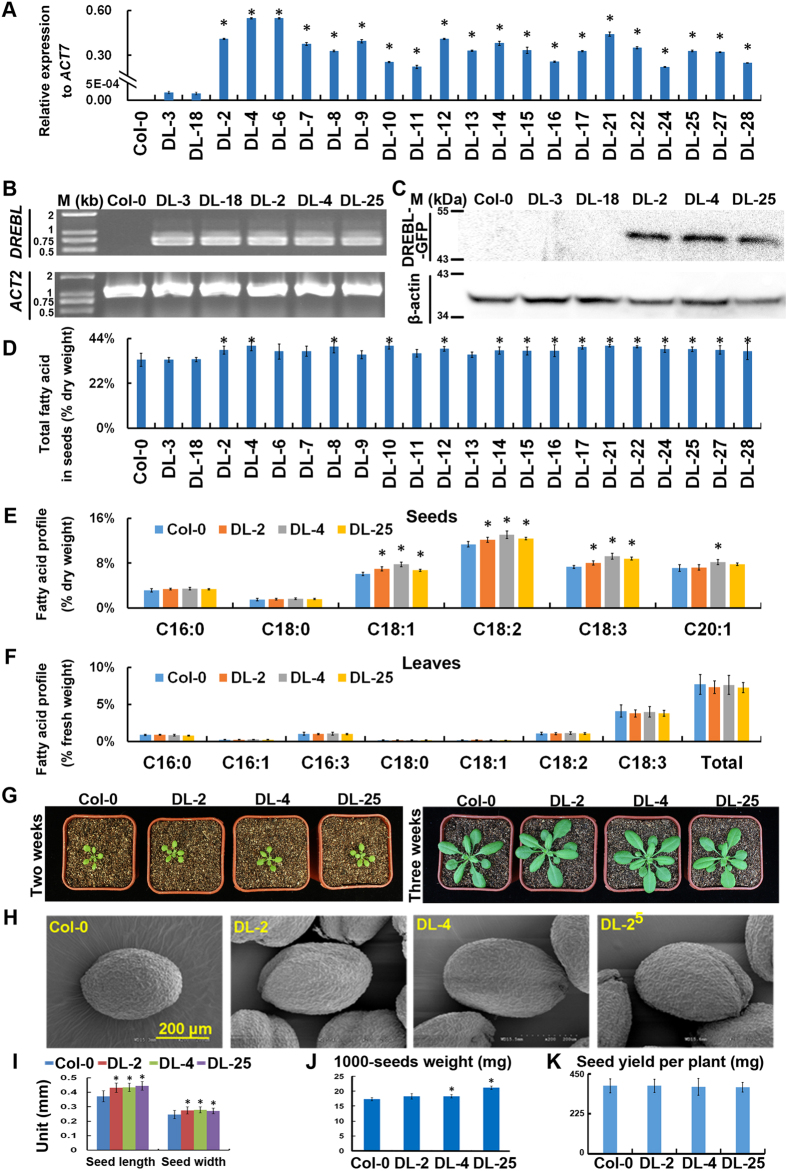
Figure 3. The effect of GmDREBL on seed-related traits.
(A) Expression of GmDREBL in transgenic plants. The relative expression level of GmDREBL was normalized using AtACTIN7 as an internal control. Bars indicate SD (n = 4). (B) Examination of GmDREBL presence by PCR in transgenic plant using genomic DNA as a template. An actin 2 gene was also amplified as the control. (C) Detection of GmDREBL-GFP in transgenic plants by Western blot analysis using mouse anti-GFP antibody. And the detection of β actin was used as the control. (D) Overexpression of GmDREBL increased total fatty acid content of transgenic Arabidopsis seeds. Bars indicate SD (n = 4). (E) The profile of fatty acids in dry seeds of Col-0 and three lines DL-2, DL-4 and DL-25. Bars indicate SD (n = 4). (F) The profile of fatty acids in fresh leaves of 12-day-old seedlings from Col-0 and three lines DL-2, DL-4 and DL-25. Bars indicate SD (n = 4). (G) The rosette phenotypes of Col-0 and three homozygous lines DL-2, DL-4 and DL-25 in two and three weeks. (H) The scanning electron micrograph of the seed coat of Col-0 and transgenic plants with GmDREBL. The white line stands for 200 μm. (G) The statistical result of seed length and seed width of wild type Col-0 plant and transgenic plants with GmDREBL. Bars indicate SD (n = 12). (I) Overexpression of GmDREBL increased 1000-seed weight of transgenic Arabidopsis seeds. Bars indicate SD (n = 4). (J) The seed yield per plant of Col-0 and three homozygous lines DL-2, DL-4 and DL-25. Bars indicate SD (n = 10). All the asterisks indicate significant difference compared to the corresponding controls (p-value < 0.05).