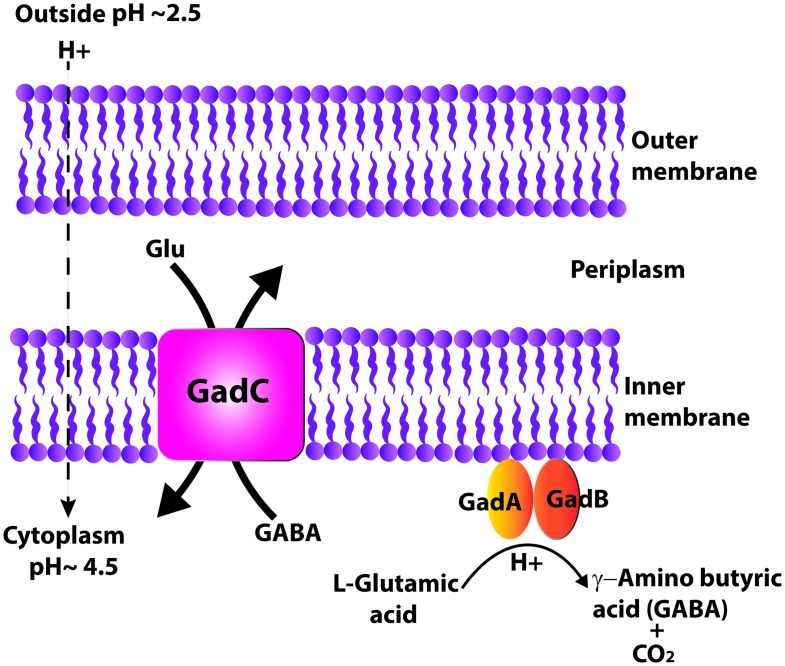
Fig 1. Schematic diagram of GDAR system (adapted from Zhao et al., 2010).
This system consists of paralogous GadA and GadB decarboxylases and an inner-membrane antiporter GadC. GadA and GadB are pyridoxal 5’-phosphate (PLP)- dependent enzymes that convert L-glutamic acid into GABA and CO2, in a reaction that consumes a cytoplasmic proton. The inner membrane antiporter GadC transports GABA out of the cell in exchange for more glutamate.