Figure 2.
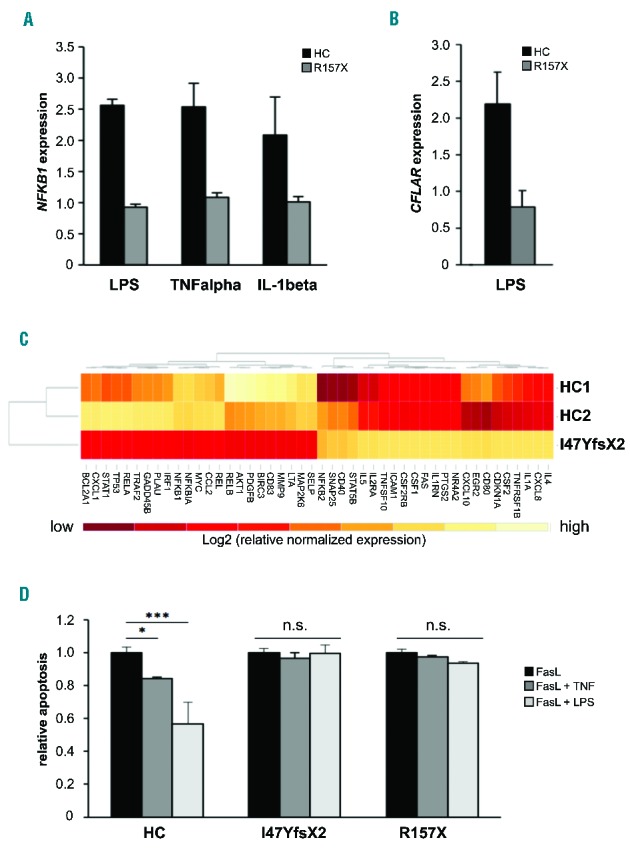
NF-κB-mediated signaling is affected in the patients. (A) Upregulation of NFKB1 mRNA expression in response to NF-κB activating stimuli is deficient in NFKB1-mutated cells. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-immortalized B cells of patient 2 and of a representative healthy control (HC) were treated for 16 h with LPS (5 μg/mL), tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) (50 ng/mL) or IL-1β (10 ng/mL). Fold change of NFKB1 mRNA expression in untreated compared to treated samples was determined by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The relative expression was normalized to the respective untreated controls (=1). GAPDH and β-actin expression were used as internal standards. Mean values of representative experiments performed in triplicate and corresponding standard deviations are shown. (B) Expression of the NF-κB target gene CFLAR (synonymous for cFLIP) is not induced by LPS in the NFKB1-mutated patients’ cells. EBV-immortalized B cells of patient 2 and healthy control cells were treated for 16 h with LPS (5 μg/mL). Fold change of mRNA expression of CFLAR was determined by real-time PCR as described in Figure 1C. (C) Differential expression of NF-κB target genes in NFKB1-mutated primary T cells of patient 1 and two healthy wild-type controls. Baseline expression of a panel of NF-κB target genes was analyzed by real-time PCR using predesigned arrays (NF-κB signaling targets RT2 Profiler PCR arrays, Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). Mean values of two independent assays are shown. High gene expression is indicated in light color, low gene expression in dark red. The analysis was supervised and results are shown scaled. (D) LPS does not protect NFKB1 mutant primary T cells from apoptosis. Primary T cells of patients 1 and 2 and healthy controls were activated by phytohemagglutinin and IL2. Cells were treated with 100 ng/mL recombinant Fas ligand to induce apoptosis in the presence or absence of 100 ng/mL LPS or 10 ng/mL TNFα. Apoptosis was determined by flow cytometric measurement of phosphatidylserine exposure indicated by binding of annexin V-FITC. Dead cells were detected with propidium iodide. Significance was tested using two-way ANoVA (*P<0,05; ***P<0,001).
