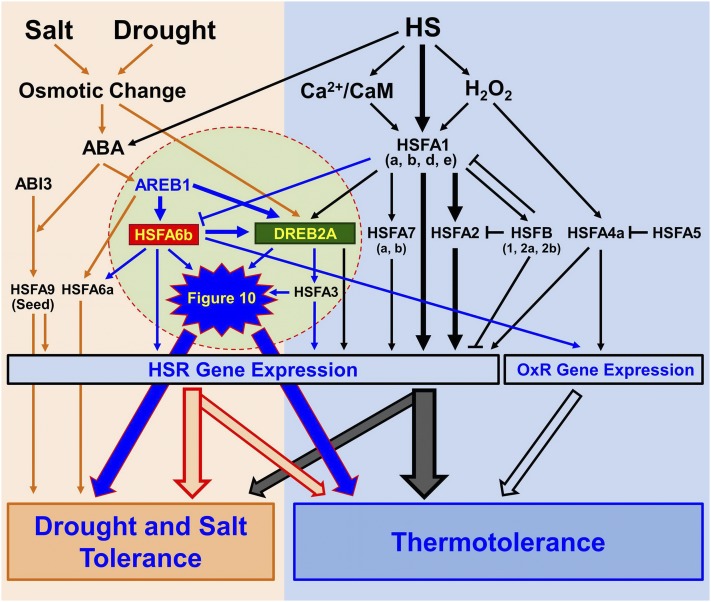
Figure 11.
Model of Arabidopsis HSFA6b as a hub connecting the ABA signaling pathway and ABA-mediated thermoprotection. CaM, Calmodulin; OxR, oxidative stress response. Under HS, activation of the HSFA1 (a, b, d, e) induces the expression of HSR genes including HSFA2 (the dominant factor), HSFA7 (a, b), as well as DREB2A and its downstream regulator HSFA3. HSFB (1, 2a, 2b) have roles in a negative feedback loop of HSR. HSFA4a is an H2O2 sensor, activating HSR and OxR gene expression. HSFA5 is the selective repressor of HSFA4a. HSFA1 (a, b, d) are negative regulators of HSFA6b. AREB1, HSFA6a, HSFA6b, and seed-specific HSFA9 are downstream regulators of the ABA-dependent pathway. HSFA6a is an activator of drought and salt response. HSFA6b acts synergistically with AREB1 for DREB2A expression, and then HSFA3 in turn is up-regulated, thus playing a role in HSR and OxR and mediating a cross talk between ABA-dependent and HSR regulons. The black and orange arrows show pathways that have been studied. The induction pathways highlighted in the circle and blue arrows emphasize the new ABA signaling pathway merging into the complex HSR network in Arabidopsis.