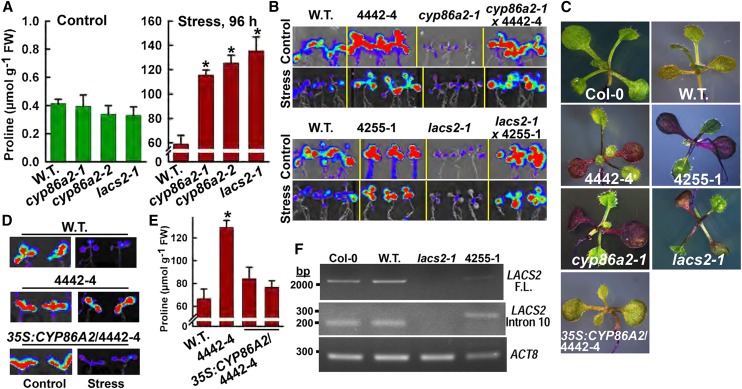
Figure 3.
4442-4 and 4255-1 are alleles of cyp86a2 and lacs2, respectively. A, Pro accumulation in two cyp86a2 T-DNA alleles and lacs2-1 under control and −1.2-MPa low ψw stress treatments. FW, Fresh weight. Data are means ± se (n = 4–6) from two experiments. Significant differences (P ≥ 0.05) compared with the wild type (W.T.) in the same treatment are marked with asterisks. B, PDH1pro:LUC2 imaging in F1 seedlings of crosses of 4442-4 and 4255-1 with cyp86a2-1 and lacs2-1, respectively, along with wild-type PDH1pro:LUC2 and mutant seedlings as controls. C, Toluidine Blue staining using seedlings of Col-0, wild-type PDH1pro:LUC2, as well as mutants and a transgenic complemented line of 4442-4. D, PDH1pro:LUC2 imaging of wild-type PDH1pro:LUC2, 4442-4, and 4442-4 complemented with 35S:CYP86A2. Stress treatment was −1 MPa for 96 h. E, Stress-induced (−1.2 MPa, 96 h) Pro accumulation in 4442-4 and two independent T3 lines of 4442-4 complemented with 35S:CYP86A2. Data are means ± se (n = 4–6) from two experiments. Significant differences (P ≥ 0.05) compared with the wild type in the same treatment are marked with asterisks. F, Reverse transcription (RT)-PCR analysis of Col-0, wild-type PDH1pro:LUC2, lacs2-1, and 4255-1 using primers to amplify the full-length LACS2 RNA or the region around intron 10. ACTIN8 (ACT8) was used as a reference gene.