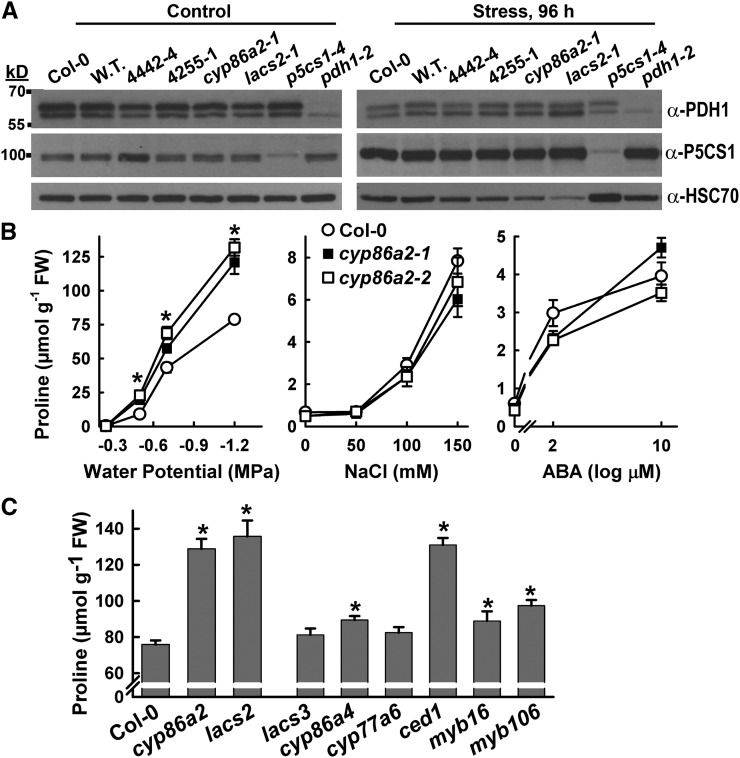
Figure 4.
Effects of cyp86a2 and lacs2 mutants on Pro metabolism and the identification of additional cuticle lipid-related mutants with increased Pro accumulation at low ψw. A, Western blots of PDH1 and P5CS1 protein levels in Col-0, wild-type PDH1pro:LUC2 (W.T.), and cyp86a2 and lacs2 mutants. p5cs1-4 and pdh1-2 were included to show the specificity of the antisera. Blots were stripped and reprobed with antisera recognizing HSC70 as a loading control. A total of 50 μg of protein was loaded in each lane. B, Effects of a range of low-ψw, salt, or abscisic acid (ABA) treatments on Pro accumulation of the Col-0 wild type and cyp86a2 mutants. FW, Fresh weight. Data are means ± se (n = 8–12) from two experiments. Significant differences (P ≥ 0.05) compared with the wild type in the same treatment are marked with asterisks. C, Stress-induced (−1.2 MPa, 96 h) Pro accumulation in cuticle metabolism mutants. Data are means ± se (n = 11–24) from two experiments. Significant differences (P ≥ 0.05) compared with the wild type are marked with asterisks. For ced1, cyp77a6, and cyp86a4, the data shown are combined from two to three T-DNA alleles that had identical phenotypes. Additional information and RT-PCR verification of T-DNA mutants can be found in Supplemental Figure S10.