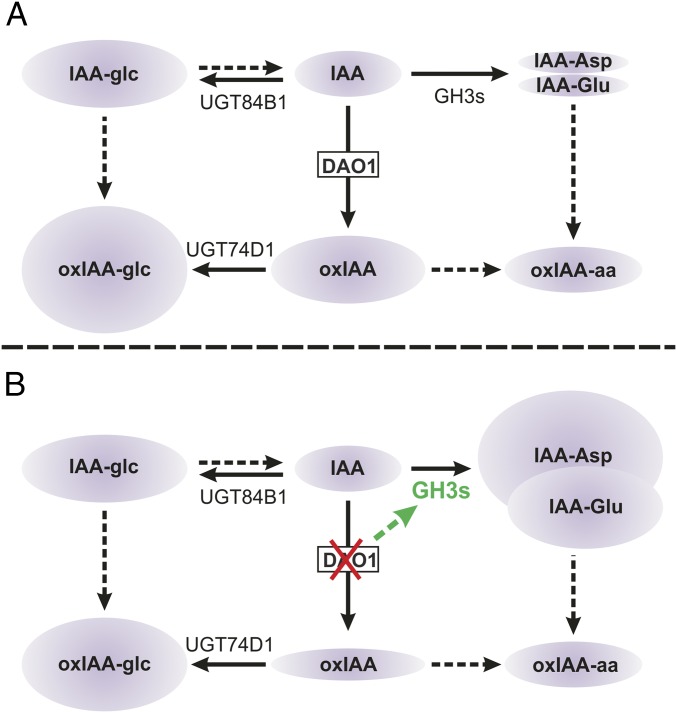
Fig. 5.
IAA degradation and conjugation regulate IAA homeostasis in Arabidopsis. (A) In WT plants, IAA is irreversibly oxidized to oxIAA by DAO1 and subsequently conjugated with glucose by the UGT74D1 enzyme to produce oxIAA-glc (9). IAA can also be conjugated to either glucose (IAA-glc) or amino acids by UGT84B1 (7) and members of the GH3 family (2), respectively. IAA-Glu and IAA-Asp are the most abundant IAA-amino acid conjugates in Arabidopsis (5, 10, 11) and believed to be irreversible conjugates that cannot be hydrolyzed to form free IAA (4, 10). (B) In the dao1-1 mutant, GH3 genes are up-regulated to drain accumulating IAA by irreversible conjugation to form IAA-Asp and IAA-Glu, whereas IAA-glc levels are unaltered. Solid arrows indicate steps in which the indicated enzyme is known to catalyze the reaction. Dashed arrows indicate steps that are not well-defined. oxIAA-aa, 2-oxoindole-3-acetic acid amino acid.