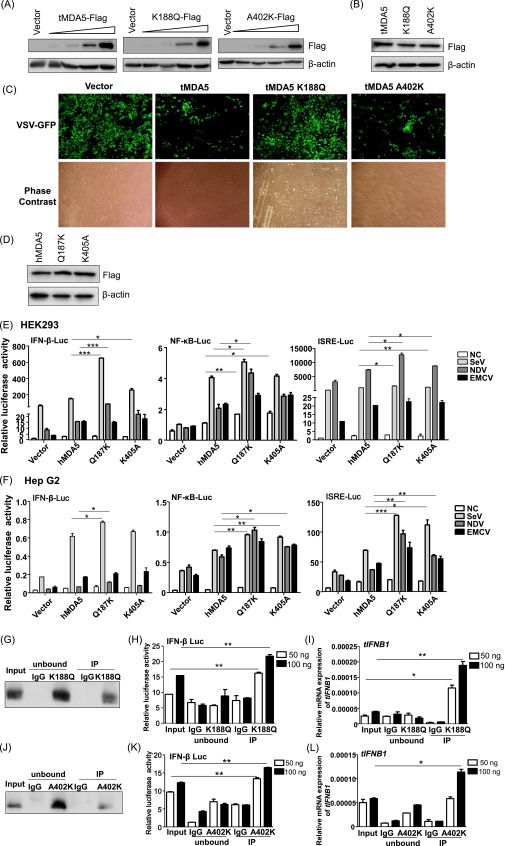
Fig. S7.
Antiviral activities of MDA5 and its mutants in TSPRCs and human cells. (A and B) Overexpression of tMDA5 and its mutants, tMDA5 K188Q and tMDA5 A402K. TSPRCs (1 × 104 cells per well) were grown in a 24-well plate overnight and were transfected with different amounts of expression vector (section A: 3.2, 16, 80, and 400 ng/well; section B: 400 ng/well) or empty vector (400 ng/well) for 36 h. Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblot using the anti-Flag antibody. Sections A and B refer to the conditions described in Fig. 5 A and B, respectively. (C) Overexpression of tMDA5 and its mutants had different abilities to inhibit vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) replication. TSPRCs (1 × 105 cells per well) were grown in a 12-well plate overnight and were transfected with the empty vector (pCMV-3Tag-8 vector, 1 μg) or indicated expression vector (1 μg) for 12 h, followed by infection with VSV-GFP (MOI = 0.01) for 12 h. Cells were photographed under an Olympus microscopy (original magnification, ×10). Data are representative of three independent experiments. (D) Overexpression of Flag-tagged hMDA5, hMDA5 Q187K, and hMDA5 K405A in the HEK293 cells. Cells (1 × 105 cells per well) were grown in 12-well plate overnight and were transfected for 48 h before the harvest. Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblot using the anti-FLAG antibody. (E and F) Overexpression of hMDA5, hMDA5 Q187K, and hMDA5 K405A on the IFN-β-Luc, NF-κB-Luc, and ISRE-Luc reporter activities upon infection with different RNA viruses in HEK293 cells (E) and Hep G2 cells (F). Cells (1 × 104 cells per well) were grown in a 24-well plate overnight and were transfected with indicated expression vector and luciferase reporter for 24 h, followed by infection with SeV (20 HAU/mL), NDV (MOI = 10) or EMCV (MOI = 1) for 12 h before the harvest for luciferase assay. (G–I) tMDA5 K188Q RNA-IP assay. TSPRCs (1 × 108 cells) were grown in a 150-mm culture dish overnight and were transfected with Flag-tagged mutant tMDA5 K188Q overexpression vector (30 μg) for 24 h, and then cells were infected with SeV (20 HAU/mL) for 16 h. The subsequent procedure was similar to that of Fig. 3 D–F. Precipitation was verified by immunoblot with the anti-Flag antibody (G). RNAs from the SeV-infected TSPRCs overexpressing the Flag-tagged tMDA5 K188Q (Input), RNAs associated with tMDA5 K188Q or IgG (control) immunoprecipitates (IP), or RNAs remaining after tMDA5 K188Q or IgG immunoprecipitations (unbound) were tested for the abilities to stimulate the IFN-β-Luc in HEK293 cells (H) or to induce tIFNB1 mRNA (normalized to the β-actin) in TSPRCs (I). Same assays were performed for mutant tMDA5 K402A (J–L). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, Student t test. Bars represent mean ± SEM. All experiments were repeated for three times, with similar results.