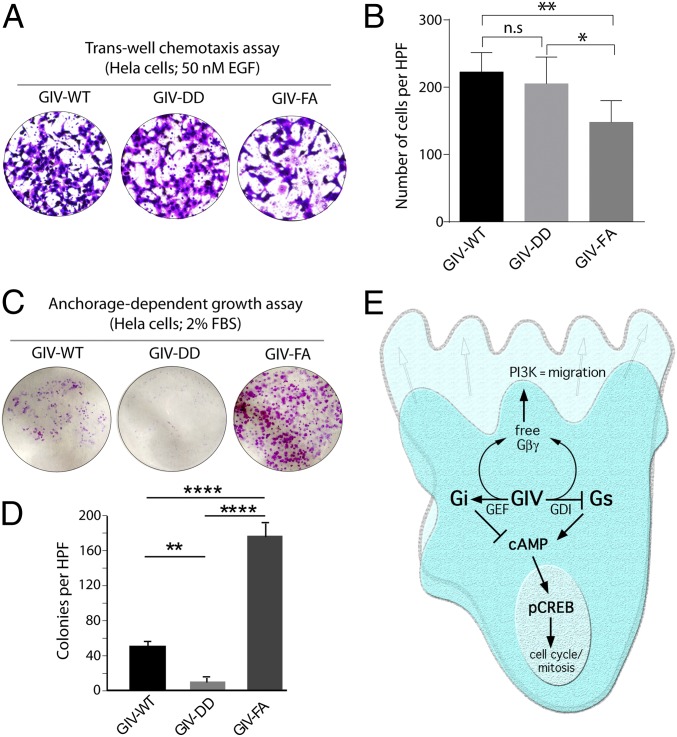
Fig. 6.
Inhibition of Gαs signaling by GIV inhibits anchorage-dependent tumor growth but does not affect cell motility/chemotaxis in HeLa cells. (A and B) GIV HeLa cell lines were analyzed for chemotaxis toward EGF using a Transwell migration assay (Experimental Procedures). After 6 h, membranes were fixed and stained with toluidine blue and imaged at 20×. (A) Representative images of high-power fields (HPF). (B) Bar graphs display the number of migrating cells per HPF (y axis) averaged from 20 HPFs per experiment; n = 3. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (C and D) The HeLa cell lines used in A were analyzed for anchorage-dependent growth on six-well plastic plates (Experimental Procedures). After 2 wk, cells were fixed and stained with crystal violet. (C) Representative images of the crystal violet-stained single wells of a six-well plate. (D) Bar graphs display the average number of colonies per HPF (y axis), as determined using the colony-counter feature of ImageJ; colonies in 20 HPFs per well from two wells per experiment were counted, n = 4. Results are expressed as ± SEM; **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001. (E) Schematic summarizing the findings of the current work integrated with previous literature on GIV’s role in the modulation of G-protein and growth factor signaling during cell migration. Previously published work (on the left) has shown that GIV triggers the activation of Gαi via an evolutionarily conserved, C-terminally located GBA motif (1). Activation of Gi has two major consequences: (i) free Gβγ heterodimers released from Gi activate the PI3K–Akt pathway (1), and (ii) activation of Gαi suppresses cellular cAMP (7). This work (on the right) shows that GIV’s GBA motif also serves as a GDI for Gαs and maintains the G protein in an inactive Gαs-GDP state. Inhibition of Gαs by GIV also releases free Gβγ (Fig. S6) and suppresses cellular cAMP, thereby synergistically potentiating both consequences of Gαi activation. Overall, GIV’s GBA motif suppresses mitogenic MAPK/ERK1/2 signals and cAMP→pCREB–mediated cell-cycle progression and enhances promigratory PI3K–Akt signals by paradoxically activating and inhibiting two opposing G proteins.