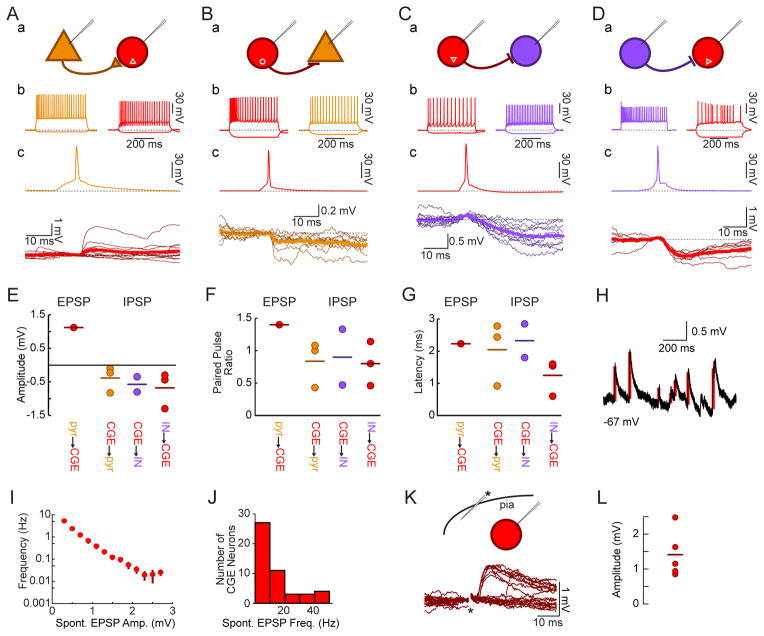
Figure 5. Transplant-Derived CGE Lineage Interneurons Form Functional Synapses with Host Excitatory and Inhibitory Neurons.
(A) Whole-cell recordings from a host pyramidal neuron (brown) and a fluorescently labeled transplanted CGE continuous adapting interneuron (red) demonstrate an EPSP onto the postsynaptic CGE-derived neuron (c, bold trace is average of 10 responses) when the presynaptic pyramidal neuron fires an action potential (c, brown).
(B) Intracellular recordings from a fluorescently labeled transplanted CGE burst nonadapting non-fast spiking interneuron (red) and a host pyramidal neuron (brown) demonstrate an IPSP onto the pyramidal neuron following action potentials elicited in the interneuron (c, bold trace is average of 10 responses).
(C) Recordings from a fluorescently labeled transplanted CGE continuous non-adapting non-fast spiking interneuron (Nkx2.1-Cre;R26-GDTA donor into an SST-Cre;R26-Ai14 host; red) and a fluorescently labeled host interneuron (purple) show an IPSP in the host interneuron (c, bold is average of 10 responses) following evoked action potentials in the CGE transplant-derived neuron.
(D) Recordings from a host interneuron (VIP-Cre;R26-Ai14 donor into a GAD67-GFP host) show an IPSP onto the transplant-derived CGE lineage continuous irregular firing interneuron (c, bold is average of 10 responses).
(E) Quantification of EPSP amplitude from a host pyramidal neuron to a transplant-derived CGE lineage interneuron (red), and IPSP amplitude of transplant-derived CGE lineage interneuron onto host pyramidal neuron (brown), transplant-derived CGE lineage interneuron onto host interneuron (purple), and host interneuron onto transplant-derived CGE lineage interneuron (red).
(F) Quantification of paired pulse ratios for postsynaptic responses to presynaptic action potentials separated by 50 ms.
(G) Postsynaptic potential onset latency quantifications.
(H) Example trace demonstrating automated EPSP detection (red bars) used in J–K.
(I) Spontaneous EPSPs onto transplanted CGE neurons are small (bar is mean±SE), though they do also receive infrequent larger inputs (ordinate is logarithmic; n=16 neurons for which >60 s of spontaneous activity were recorded).
(J) All CGE transplant-derived neurons (n=48) received spontaneous EPSPs.
(K) Extracellular minimal stimulation in cortical layer I (asterisk) reliably generates EPSPs onto a CGE transplant-derived neuron (amplitude 0.89±0.08 mV for driven vs. 0.65±0.41 mV for spontaneous EPSPs, p>0.05). Short latency EPSPs were routinely seen with layer I stimulation (7 of 7 CGE neurons tested, latency 4.7±1.3 ms).
(L) Amplitude of EPSP evoked by layer I stimulation with the postsynaptic neuron held at −70 mV (n=5 neurons, 1.41±0.33 mV).