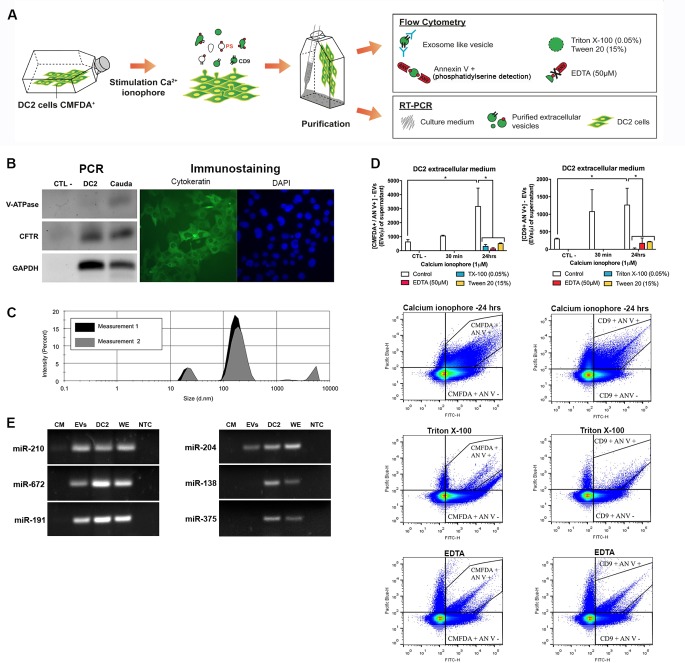
Fig 2. Secretion of Dicer1-dependent miRNAs from DC2 cells via extracellular vesicles (EVs).
(A) Schematic view of DC2 derived EVs analysis. DC2 cells were cultured, labelled with CMFDA dye and stimulated with calcium ionophore to induce EVs production. EVs were characterized according to i) their surface antigens (e.g. CD9 marker, phosphatidylserine (PS) by flow cytometry, and to ii) their miRNA content by RT-PCR. (B) Detection of Cftr (principal cell marker) and Atp6v1b1 (B1 V-ATPase subunit, clear cell marker) in cauda epididymis and DC2 cell line extracts by end-point PCR. Immunostaining for cytokeratin (green) on DC2 cells. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. (C) Size distribution of EVs released from DC2 cells in culture measured in a Zetasizer. This plot is representative of acquisitions performed twice on three distinct biological replicates. (D) Detection of CMFDA-positive EVs released from CMFDA-labeled DC2 cells by High-Sensitivity Flow Cytometry (HS-FCM). Supernatants from DC2 cells stimulated or not with 1 μM calcium ionophore for 30 min or 24 h were analyzed by HS-FCM for EV detection after annexin V (phosphatidylserine detection) and CD9 labeling. Controls include Triton X-100 0.05% that solubilizes most membranous particles, and EDTA 50 μM that inhibits annexin V labelling. (E) Detection of Dicer1-dependent miRNAs in DC2-derived EVs by end-point PCR in cells, whole tissue, and extracellular medium extracts. CM: culture medium; EVs: purified extracellular vesicles; DC2: culture medium-free DC2 cells; WE: whole epididymis; NTC: no-template control.