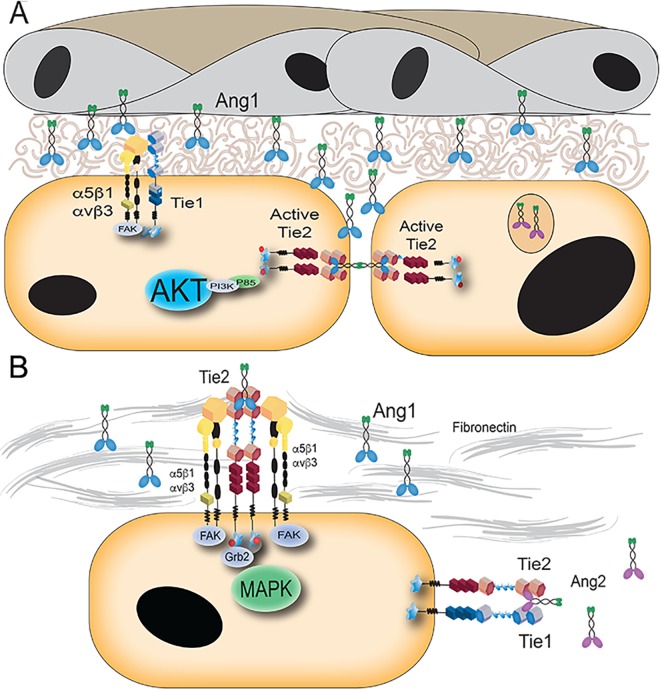
Fig 6. Proposed model of Integrin Tie2 cooperative signaling in endothelial cell regulation.
(A) Based on previous studies, it is known that Ang-1 clusters Tie2 at cell-cell junctions in endothelial cells while providing pro-survival signals through the AKT and Survivin signal transduction pathway [30,46,47]. Alternatively, Tie1 may associate with integrins, including either αVß3 or α5ß1, which are preferentially localized at the cell interface with the basement membrane containing extracellular matrix components. A link between Tie1 and the extracellular matrix could explain a role for Tie1 in vessel integrity and sheer stress that has previously been described [43–45]. (B) When Tie2 is not at junctions, it is likely capable of associating with integrins. Activation of integrin-associated Tie2 via Ang-1 and fibronectin may enrich signaling through MAPK to further facilitate endothelial cell migration and proliferation.