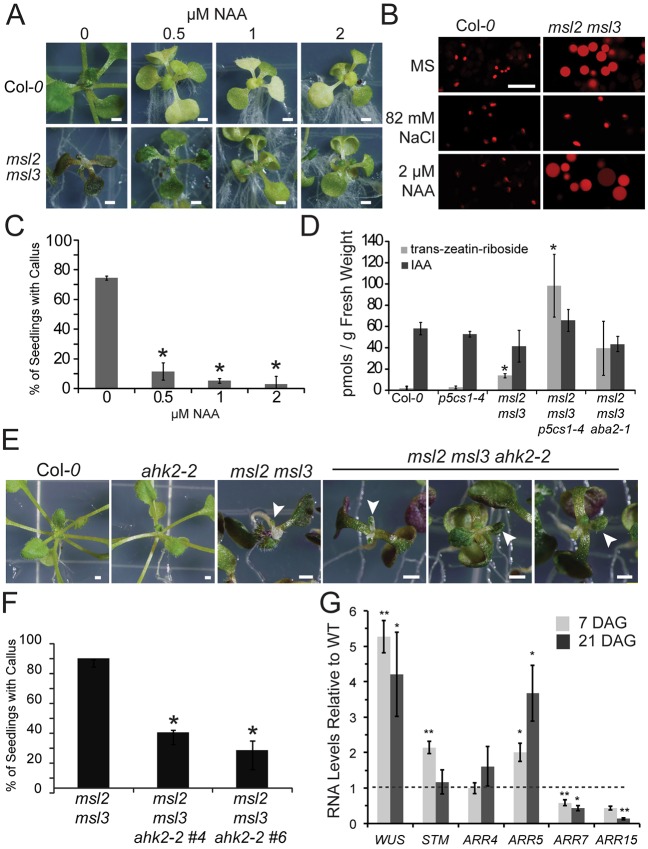
Fig. 3.
Callus produced in msl2 msl3 mutants is associated with increased CK production and requires CK signaling. (A) Seedlings grown for 21 days on solid medium containing the indicated concentration of NAA. (B) Confocal micrographs of non-green plastids in the first true leaf of msl2 msl3 mutants harboring the RecA-dsRED plastid marker and grown on indicated medium. (C) Percentage of msl2 msl3 mutants exhibiting callus when grown on NAA. The average of three biological replicates of ≥20 seedlings each is presented. Statistical groups were determined by ANOVA followed by Tukey's HSD test, P<0.01. (D) Trans-zeatin-riboside and IAA levels of 21-day-old seedlings determined by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry analysis as in Chen et al. (2009). The average of three biological replicates of ≥30 seedlings each is presented. Error bars indicate s.d. *P<0.01 compared with wild type (Student's t-test). Images of seedlings (E) and callus production (F) in msl2 msl3 ahk2-2 triple mutant and parental lines. White arrows mark deformed leaves. The average of four biological replicates of ≥20 seedlings each is presented. Error bars indicate s.e.m. *P<0.01, compared with msl2 msl3 (Student's t-test). (G) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of gene expression in the msl2 msl3 mutant. The average of three biological replicates (two technical replicates; n≥25 seedlings each) is presented. Error bars indicate s.e.m. **P≤0.05, **P≤0.01 compared with wild type of same age (Student's t-test). Scale bars: 1 mm (A,E), 10 µm (B).