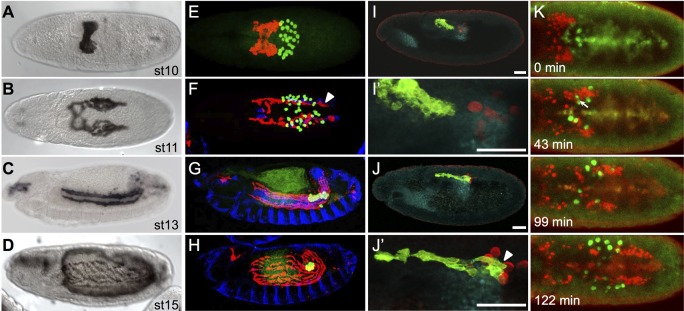
Fig. 1.
CVM cell and PGC migrations overlap spatiotemporally. (A-D) Wild-type Drosophila embryos of the indicated stages expressing the CVM-specific reporter GV2 (HLH54F>Gap-Venus) detected with an anti-GFP antibody and DAB colorimetric staining. (E-J′) Colocalization of CVM cells relative to PGCs, TVM and/or pmg in wild-type embryos containing the GV2 reporter. anti-GFP, anti-Vasa, anti-FasIII and anti-Hb9 antibodies were used to detect CVM cells (red, E-H; green, I-J′), PGCs (green, E-H; red, I-J′), TVM (blue, E-H) or midgut primordium (cyan, I-J′), respectively. (A,B,E,F) Dorsal views; (C,D,G-J′) lateral views. In this and subsequent figures, all embryos are oriented with anterior to the left and dorsal side up unless otherwise noted. E-H are stage matched to A-D. Arrowheads (F,J′) indicate CVM cells elongated in the anterior-posterior orientation. Scale bars in I′ and J′ indicate relative magnification to images I and J, respectively. (K) Movie stills from live imaging of wild-type embryos containing PGC (vasa-GFP) and CVM cell (HLH54F>H2A-mCherry, ‘HC3’) reporters, visualized over the course of 3 h from a dorsal view (see Movie 1). Movie initiates at stage 10 (time 0 min) and continues for ∼3 h until germband elongation occurs at stage 12. Arrow (43 min) indicates the position of a germ cell deforming to move between CVM cells.