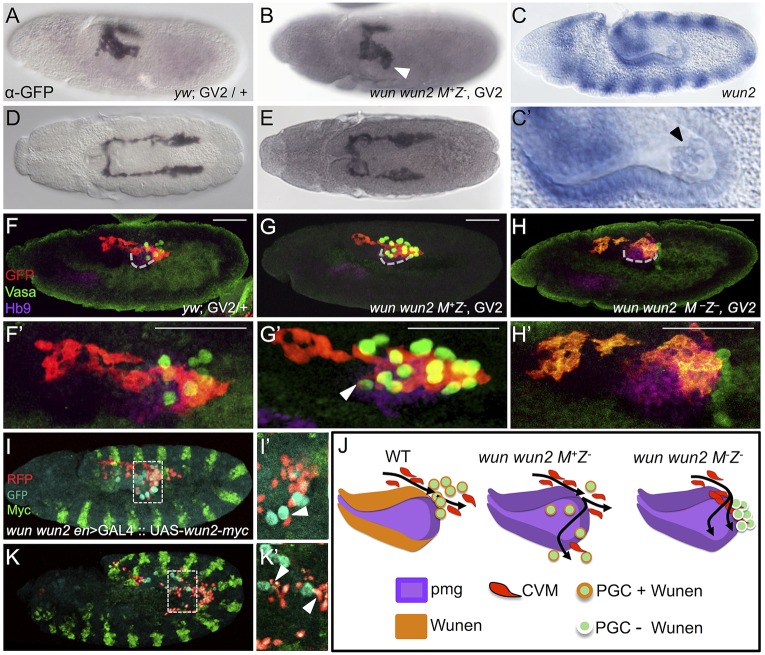
Fig. 2.
CVM cell migration is more strongly affected by the loss of maternal than zygotic wunen genes. (A,B,D,E) Wild-type (A,D) and wun wun2 zygotic (B,E) embryos expressing the CVM reporter GV2 (heterozygous) detected with anti-GFP antibody and DAB staining. (A,B) Early stage 11 embryos oriented dorsolaterally showing migration of the CVM along the lateral side of the pmg in wun wun2 zygotic mutants (arrowhead in B) compared with wild type (A). (D,E) Late stage 11 embryos, dorsal view, showing CVM cell migration in wun wun2 zygotic mutants (E) compared with wild type (D). (C,C′) In situ hybridization using a riboprobe to wun2 within a stage 10 embryo, lateral view. C′ is a magnified view of PGCs within the pmg; the arrowhead indicates wun2 expression within the germ cells. (F-H′) Lateral views of early stage 11 embryos containing the GV2 reporter of wild-type (F,F′), wun wun2 M+Z− (G,G′) or wun wun2 M−Z−(H,H′) backgrounds in which antibodies to GFP (red), Vasa (green) and Hb9 (purple) were used to assay colocalization of CVM cells, PGCs and the pmg, respectively. Dashed gray line (F,G,H) marks the ventral side of pmg. Arrowhead (G′) indicates CVM cells that have migrated almost to the ventral side of the pmg, colocalized with a mislocalized PGC. Scale bars in F'-H' show relative magnification to images in F-H. (I,I′,K,K′) Lateral view of stage 11 (I,I′) and stage 12 (K,K′) wun wun2 M+Z− en>GAL4::UAS-wun2-myc; HC3 embryos with fluorescent antibody detection of CVM (anti-RFP, red), PGC (anti-Vasa, cyan) and ectopic Wun2 (anti-Myc, green). I′ and K′ show a single z-slice from I and K, respectively. Arrowheads indicate CVM cells that are mismigrating downwards (dorsally, at this stage; I') or laterally (K′) near mismigrated PGCs. (J) Model showing the aberrant movement of CVM cells and PGCs in the absence of zygotic wun wun2 (G) and both maternal and zygotic wun wun2 (H) compared with wild type (F).