Fig. 9.
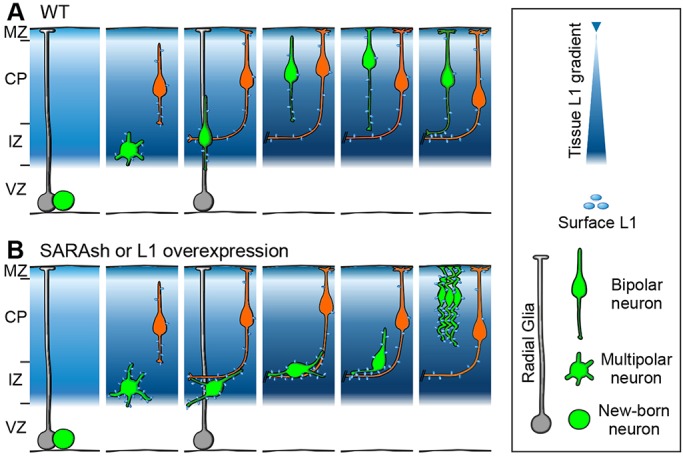
Summary of major findings. Diagrams depict the migration of postmitotic neurons in the developing neocortex. The blue background represents the expression level of L1. The asymmetric division of an RG cell gives rise to one RG cell (gray) with a radial process touching the pial surface, and one neuron (green) with multipolar, and later, bipolar neurites. Intermediate basal progenitors are omitted for simplicity. (A) Wild-type neuron undergoes radial migration through the IZ en route to the CP. (B) SARA-suppressed or L1-overexpressing migrating neurons display disorientated soma/LP, delayed multipolar-to-bipolar transition and IZ crossing. These defects are likely to be due to the increased surface L1 in the LPs, resulting in transhomophilic or transheterophilic (not shown) interaction with tangentially growing axons at the IZ (orange) or other migrating neurons (not shown). SARA-suppressed neurons are eventually able to overcome the IZ retention and reach the more superficial CP layers. The LPs of these neurons appear highly curved, presumably due to increased L1-mediated cell-cell and/or cell-ECM adhesion.
