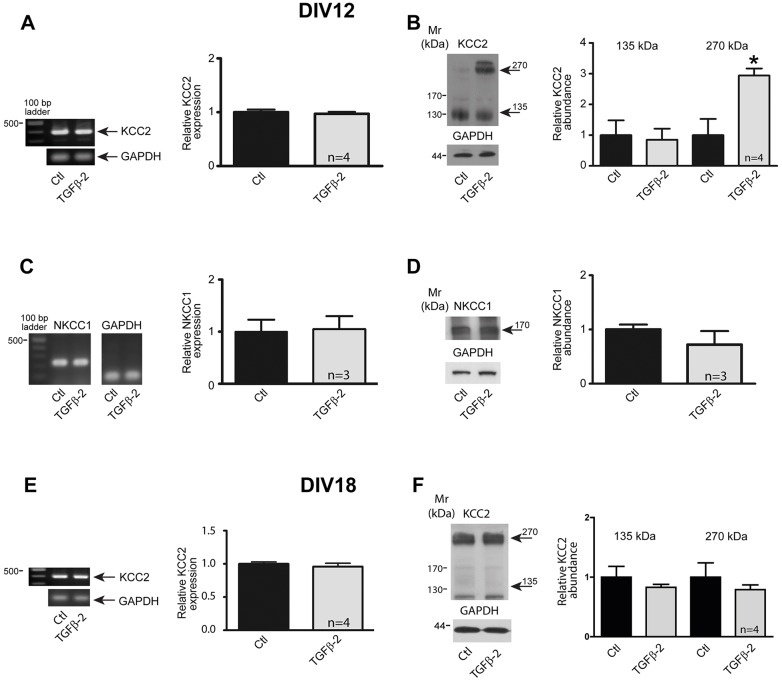
Fig. 1.
Regulation of KCC2 in neurons at different developmental stages by TGF-β2. (A) Developing (DIV12) cultured mouse hippocampal neurons were treated with 2 ng/ml TGF-β2 for 60 min. KCC2 transcript (397 bp) expression was normalized to GAPDH by semi-quantitative RT-PCR. Data are given as fold changes compared to control. (B) DIV12 cultured neurons were treated with TGF-β2 before immunoblotting with anti-KCC2 antibody. Arrows point to the ∼135 kDa and ∼270 kDa KCC2 bands. The ratio of KCC2:GAPDH immunoreactivity was determined. *P=0.016 relative to control as assessed by an unpaired t-test (n=4). (C,D) DIV12 cultured mouse hippocampal neurons were treated with 2 ng/ml TGF-β2 for 60 min followed by by semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis (C) or immunoblotting (D). The ratio of the NKCC1:GAPDH transcript expression (in control set to 1) and the ratio of the NKCC1:GAPDH immunoreactivity were then determined. (E) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis in more mature (DIV18) cultured mouse hippocampal neurons treated with 2 ng/ml TGF-β2 for 60 min, (n=4). (F) Immunoblot analysis for ∼135 kDa (arrow) and ∼270 kDa (arrow) KCC2 protein in cultures of more mature hippocampal neurons upon TGF-β2 treatment. Data are given as mean±s.e.m. for the indicated number of experiments.