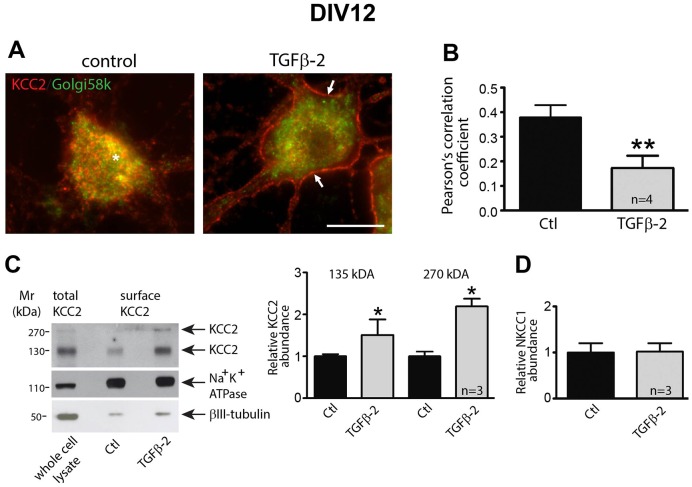
Fig. 2.
KCC2 membrane trafficking in hippocampal neurons is controlled by TGF-β2. (A) Mouse hippocampal neurons cultured for 12 days were treated for 60 min with 2 ng/ml TGF-β2, followed by immunolabeling for KCC2 (red) and the Golgi marker Golgi58k (green). The asterisk indicates intracellular KCC2–Golgi58k colocalization and the arrows point to membrane KCC2 labeling. Scale bar: 10 µm. (B) Colocalization of KCC2 and Golgi58k was quantified by determination of the Pearson's correlation coefficient. **P=0.0015 compared to the control condition (unpaired Student's t-test). (C,D) Cultured neurons were treated with TGF-β2 for 60 min followed by biotinylation of surface proteins. The ratio of ∼135 kDa surface KCC2:total KCC2, ∼270 kDa surface KCC2:total KCC2 (C), and of surface NKCC1:total NKCC1 (D) in untreated (Ctl) and TGF-β2-treated cultures were then determined and presented relative to values for controls (set to 1). *P=0.014 compared to the control condition (unpaired Student's t-test). Data are given as mean±s.e.m. from three or four independent experiments as indicated.