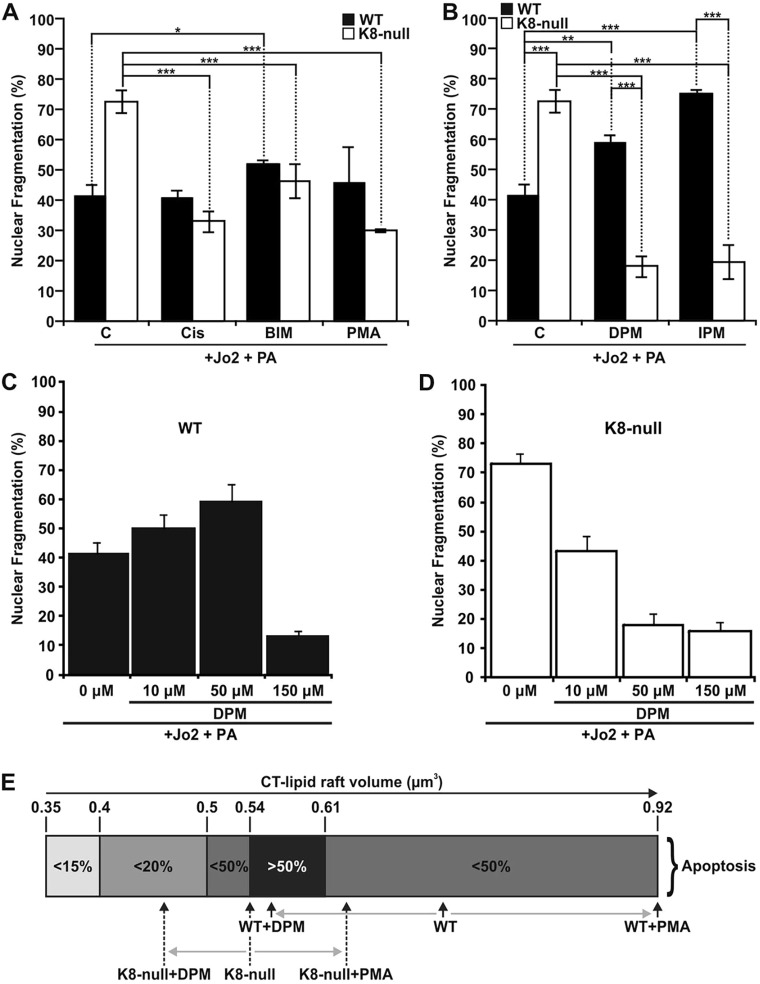
Fig. 7.
K8/K18 IF-dependent lipid raft size as a modulatory parameter of FasR-mediated apoptosis. (A) Nuclear fragmentation assessments in response to a Jo2 (0.5 µg/ml)+Protein A (PA, 0.1 µg/ml) treatment of WT and K8-null hepatocyte for 7 h with or without a 1 h pre-treatment with PKC activators [5 µg/ml cisplatin (Cis) or 100 nM PMA] or PKC inhibitor (1 µM BIM), showing that PKC modulations affect FasR-dependent nuclear fragmentation (C, untreated control). (B) Nuclear fragmentation analysis following a Jo2 (0.5 µg/ml)+Protein A (PA, 0.1 µg/ml) treatment of WT and K8-null hepatocytes for 7 h without or with a 1 h pre-treatment with ASMase inhibitors (50 µM DPM or 50 µM IPM,), indicating that ASMase inhibition affects FasR-dependent nuclear fragmentation (C: untreated control). (C,D) Nuclear fragmentation assessments in response to a Jo2 (0.5 µg/ml)+Protein A (PA, 0.1 µg/ml) treatment for 7 h with or without a pre-treatment with the ASMase inhibitor DPM at different concentrations in WT (C) or K8-null (D) hepatocytes. (E) Scale representation of the optimal range of CT-lipid raft volume for seeing apoptosis, showing where WT and K8-null hepatocytes are positioned on the scale versus different treatment conditions. Quantitative results are mean±s.e.m. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.005 (t-test).