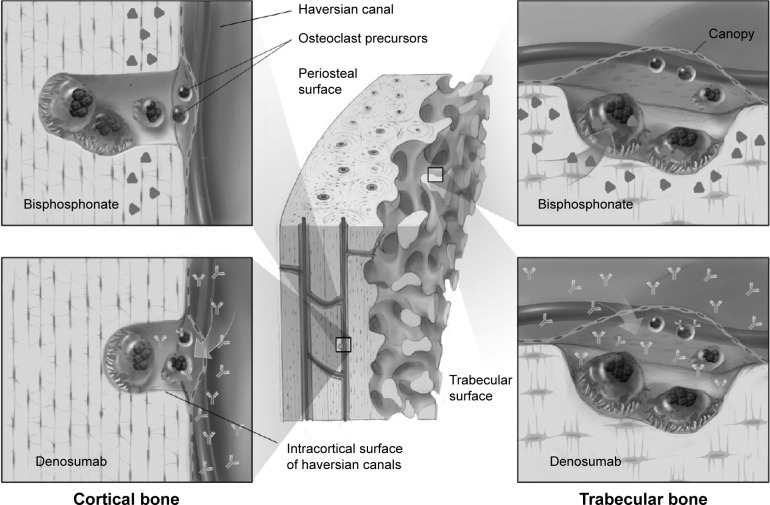
Figure 5.
In trabecular bone, osteoclasts engulf matrix containing alendronate, whereas denosumab accesses osteoclasts via the extracellular fluid.
Notes: Because cortical bone has a low surface area/mineralized bone matrix volume, alendronate cannot be adsorbed as readily into the cortical compartment. In contrast, denosumab is not adsorbed onto mineralized bone matrix but circulates freely, thus inhibiting resorption of cortical and trabecular bone more equally.