Figure 1.
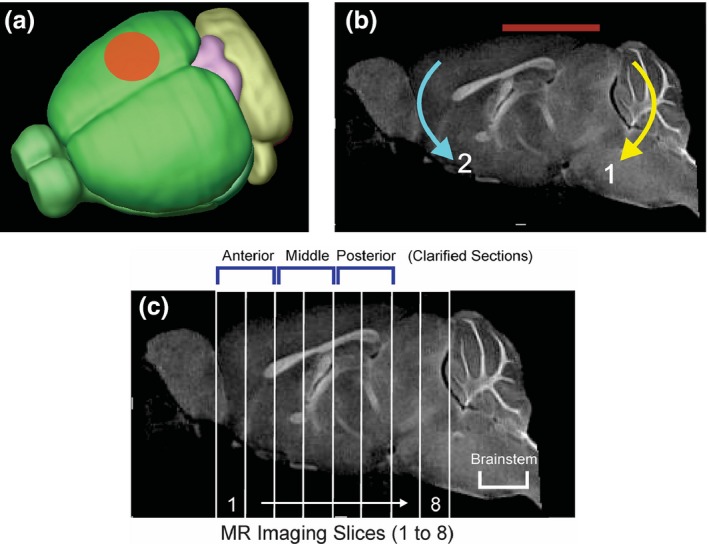
Closed Head Injury (CHI) model. (a) CHI was performed over the right hemisphere between bregma and lambda with a 4 mm diameter pneumatically driven piston. (b) The mouse was placed on a foam bed where the impactor displaced the cranium resulting in a rotational displacement of the brain (red line indicates impact zone). Initial impact causes rotation (1) followed by a secondary rotation (2). (c) A sagittal MR image illustrating the ~ 1 mm thick coronal sections from which T2‐weighted imaging (T2WI) analysis was performed. Six of the MRI slices corresponded to the three ~ 2 mm clarified brain sections: anterior (MRI sections 1–2), middle (MRI sections 3–4) and posterior (MRI sections 5–6) used for microglial morphologic analysis. In addition, the brainstem was also assayed for microglial morphology. The impact site was centered on MRI sections 4–6.
